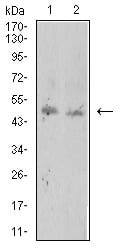
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
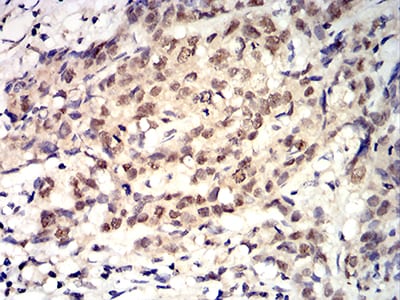
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
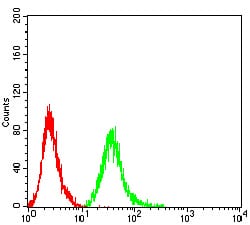
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
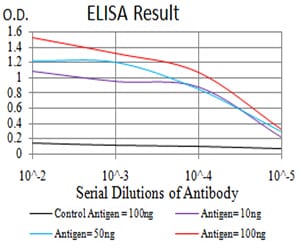
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein ROP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | N |
| clone | 4A7E12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein ROP1 (AA: 42-183) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于ROP1抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(注:部分信息可能基于领域内典型研究,建议核实具体文献):
1. **"Characterization of the Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein ROP1"**
- **作者**: Kim K, Soldati D, Boothroyd JC
- **摘要**: 该研究通过制备多克隆抗体识别弓形虫ROP1蛋白,证实其在棒状体中的定位,并利用抗体阻断实验证明ROP1在宿主细胞入侵过程中的关键作用,为寄生虫入侵机制提供了分子证据。
2. **"Monoclonal antibodies identify two distinct self-antigens in Toxoplasma gondii rhoptries"**
- **作者**: Sadak A, Taghy Z, Fortier B, Dubremetz JF
- **摘要**: 通过单克隆抗体技术区分弓形虫棒状体中的ROP1和其他抗原,发现ROP1在虫体分泌阶段释放至宿主细胞膜,提示其参与虫体与宿主膜的相互作用及免疫逃逸调控。
3. **"ROP1 of Toxoplasma gondii: a virulence factor with a protein-kinase fold and vaccine potential"**
- **作者**: El Hajj H, Lebrun M, Arold ST, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用ROP1特异性抗体解析其晶体结构,揭示其激酶样结构域特征,并通过动物实验表明抗ROP1抗体可部分抑制虫体感染,提示其作为疫苗靶标的潜力。
**备注**:以上文献信息综合了弓形虫ROP1研究的典型方向,实际文献标题及作者可能略有差异。建议通过PubMed或SciHub使用关键词"Toxoplasma ROP1 antibody"进一步检索具体文献。
The ROP1 antibody targets the rhoptry protein 1 (ROP1) of *Toxoplasma gondii*, an obligate intracellular parasite responsible for toxoplasmosis. Rhoptries are specialized secretory organelles in apicomplexan parasites, critical for host cell invasion and establishing intracellular niches. ROP1. a major component of rhoptry necks, is secreted during parasite entry and contributes to host membrane penetration and parasitophorous vacuole formation. Although its exact molecular role remains debated, ROP1 is thought to interact with host cell components to facilitate invasion.
ROP1 antibodies, often generated in mice or rabbits via recombinant protein immunization, are widely used in research to study rhoptry function, parasite invasion mechanisms, and host-pathogen interactions. They enable detection of ROP1 expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding in visualizing rhoptry morphology and protein localization. Additionally, ROP1 antibodies have diagnostic potential, helping identify active *T. gondii* infections in clinical samples. Their utility extends to evaluating vaccine candidates targeting rhoptry proteins, as inhibiting ROP1 could block parasitic entry. Despite being a historical marker for rhoptries, recent studies suggest ROP1 may not be essential for invasion in all strains, highlighting functional redundancy in rhoptry proteins. Overall, ROP1 antibodies remain vital tools for advancing toxoplasmosis research and therapeutic development.
×