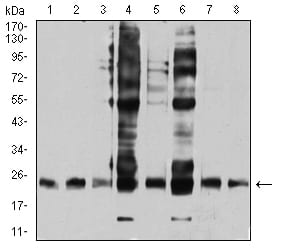
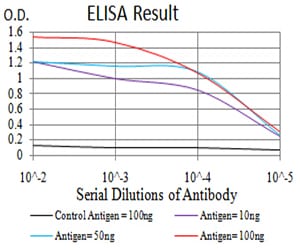
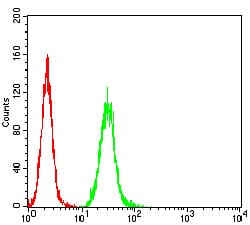
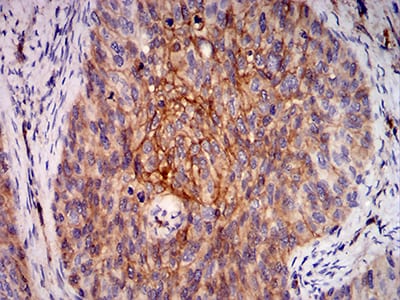
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Entrez GeneID | 5899 |
| clone | 7F8B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human RALB (AA: 89-206) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于RALB抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Distinct roles for RalA and RalB in tumor invasion and metastasis*
**作者**:Feig, L.A. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过使用特异性RALB抗体,发现RALB激活对肿瘤细胞的侵袭性至关重要,通过调节细胞迁移相关通路(如MAPK/ERK),而RALA主要影响增殖。
2. **文献名称**:*RalB mediates pro-survival autophagy in cancer cells*
**作者**:Lim, K.H. et al.
**摘要**:利用RALB抗体敲低实验,揭示RALB通过激活自噬相关蛋白(如Beclin-1),在营养缺乏条件下维持癌细胞存活,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*RalB regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer*
**作者**:Moskalenko, S. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫沉淀(使用RALB抗体)发现,RALB与IKK复合物相互作用,促进NF-κB通路的激活,驱动胰腺癌的炎症反应和化疗抵抗。
4. **文献名称**:*Ral GTPases regulate exocyst-mediated trafficking of receptor tyrosine kinases*
**作者**:Peschard, P. & McCarthy, A.
**摘要**:研究利用RALB特异性抗体证明,RALB通过调控外泌体复合物,影响EGFR等受体的内吞和降解,从而调节癌细胞信号传导和生长。
这些文献均通过RALB抗体的实验手段,揭示了RALB在肿瘤侵袭、自噬、炎症信号及受体运输中的关键作用。
RALB (RAS-like proto-oncogene B) is a member of the RAS superfamily of small GTPases, which function as molecular switches regulating diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, survival, and migration. Unlike its homolog RALA, RALB is particularly implicated in cancer progression, where it promotes invasion, metastasis, and resistance to therapies. RALB achieves this by interacting with downstream effectors such as exocyst complex components (e.g., SEC5 and EXO84) to modulate vesicle trafficking, cytoskeletal dynamics, and immune evasion pathways. Its oncogenic activity is often linked to hyperactivation via mutations in upstream regulators (e.g., RAS, EGFR) or overexpression in tumors like pancreatic, lung, and colon cancers.
RALB-targeting antibodies have emerged as tools to study its function or potentially inhibit its signaling in cancer. These antibodies typically recognize specific epitopes on RALB, enabling applications in Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunoprecipitation to map its interactions and activation status. Therapeutic RALB-neutralizing antibodies are under exploration to disrupt RALB-effector binding or block GTPase activation, though challenges remain in achieving selectivity over RALA due to their high structural similarity. Recent studies also highlight RALB’s role in autophagy and tumor immune microenvironments, broadening its relevance as a biomarker or therapeutic target. Advances in antibody engineering, such as nanobodies or bispecific formats, may improve targeting efficacy against this elusive oncoprotein.
×