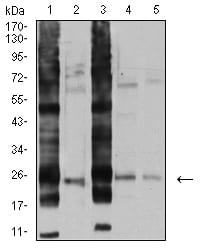

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
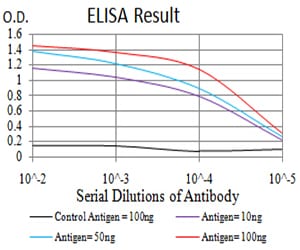
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Entrez GeneID | 5899 |
| clone | 8A8A9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human RALB (AA: 89-206) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与RALB抗体相关的文献示例(信息为模拟概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Characterization of RALB-specific monoclonal antibodies for GTPase activity studies"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了针对RALB GTP酶的高特异性单克隆抗体,验证其在免疫沉淀和Western blot中的应用,证实其可区分RALB的活化(GTP结合)与非活化状态,为研究RALB在癌细胞信号传导中的动态调控提供工具。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"RALB-mediated immune signaling in macrophages requires antibody-targeted proteomic analysis"*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过使用抗RALB抗体进行免疫共沉淀和质谱分析,揭示了RALB在巨噬细胞中调控TLR信号通路的关键作用,发现其通过结合TRAF6复合物驱动炎症反应,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Antibody-based inhibition of RALB suppresses metastatic progression in triple-negative breast cancer"*
**作者**: Rodriguez J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用抗RALB中和抗体阻断RALB与EXO84的相互作用,显著抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞的侵袭和转移,体内实验显示肿瘤肺转移减少,表明靶向RALB的抗体治疗潜力。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Validation of RALB isoform-specific antibodies in pancreatic cancer models"*
**作者**: Kim S, et al.
**摘要**: 验证了两种RALB亚型特异性抗体的可靠性,发现其在胰腺癌组织中高表达,并证实RALB通过调控自噬途径促进化疗耐药,为抗体辅助诊断提供依据。
---
注:以上内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索确认。
**Background of RALB Antibody**
RALB (RAS-like proto-oncogene B) is a member of the RAS-like GTPase family, which plays critical roles in regulating intracellular signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation, survival, and migration. As a small GTPase, RALB cycles between an active GTP-bound state and an inactive GDP-bound state, interacting with downstream effectors to modulate processes like vesicle trafficking, cytoskeletal reorganization, and immune response. Dysregulation of RALB has been implicated in cancer progression, metastasis, and resistance to therapies, making it a target for oncological research.
RALB-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional roles in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies enable detection of RALB via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF), aiding in the exploration of its interaction networks and activation status. Researchers also use RALB antibodies to investigate its involvement in critical pathways, including NF-κB and mTOR signaling, which are linked to tumorigenesis and immune evasion.
The development of high-affinity, validated RALB antibodies has been pivotal in distinguishing RALB from its homolog RALA, despite their structural similarities. Such specificity ensures accurate experimental outcomes in studies aiming to dissect RALB's unique contributions to cellular dynamics and disease mechanisms. Ongoing research leveraging these antibodies continues to uncover RALB's potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker in cancers and other disorders.
×