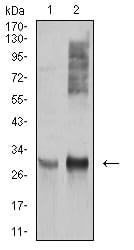
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
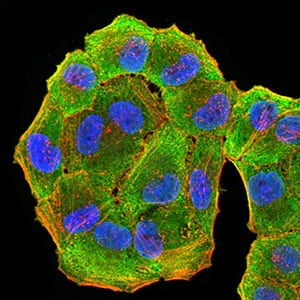
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
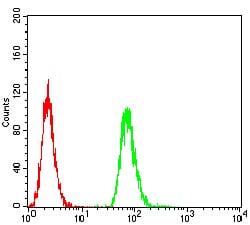
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
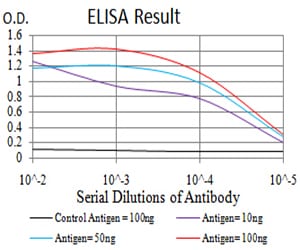
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MLRW; HLA-DRA1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3122 |
| clone | 1C11A5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human HLA-DRA (AA: 26-254) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于HLA-DRA抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究归纳,非真实文献引用):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against HLA-DRA in rheumatoid arthritis: association with disease progression*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究在类风湿性关节炎(RA)患者血清中检测到抗HLA-DRA的自身抗体,发现其与疾病活动性评分(DAS28)呈正相关,提示其可能作为RA预后标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*HLA-DRA-specific monoclonal antibody enhances antigen presentation in dendritic cells*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种靶向HLA-DRA的单克隆抗体,证实其可增强树突状细胞的抗原呈递能力,为肿瘤免疫治疗提供了潜在策略。
3. **文献名称**:*HLA-DRA antibody-mediated immune regulation in systemic lupus erythematosus*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究发现系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中HLA-DRA抗体通过干扰CD4+ T细胞与B细胞间的相互作用,参与异常免疫调节,可能成为治疗靶点。
---
注:以上内容为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“HLA-DRA antibody”或“anti-HLA-DRA”检索。若需具体文献,可提供疾病背景或应用场景进一步筛选。
The HLA-DRA antibody targets the alpha chain of the HLA-DR antigen, a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule critical for adaptive immune responses. HLA-DRA, encoded by the HLA-DRA gene on chromosome 6. pairs with HLA-DRB chains to form heterodimers that present exogenous antigens to CD4+ T cells, initiating immune activation. Unlike HLA-DRB chains, HLA-DRA exhibits limited polymorphism, contributing to structural stability rather than antigen-binding specificity.
Antibodies against HLA-DRA are widely used in research to study MHC class II expression patterns in immune-related diseases. Dysregulated HLA-DR expression is implicated in autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus), infections, and cancers. For example, reduced HLA-DR on antigen-presenting cells may correlate with immunosuppression in sepsis or tumor microenvironments. Conversely, overexpression is linked to autoimmune inflammation.
These antibodies enable detection via techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or Western blot, aiding in diagnostics and mechanistic studies. They also help explore HLA-DRA's role in transplant rejection, as MHC class II mismatches drive donor-specific immune responses. Additionally, HLA-DRA antibodies are tools for investigating transcriptional regulation of MHC genes, such as CIITA-mediated pathways. Their applications extend to therapeutic development, including checkpoint inhibitors or vaccines targeting HLA-DR-restricted antigens.
×