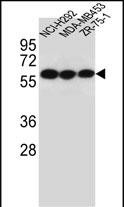
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
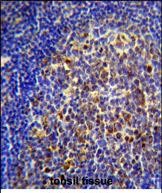
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-10, Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-10, NACHR alpha-10, CHRNA10, NACHRA10 |
| Entrez GeneID | 57053 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CHRNA10 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 179-206 amino acids from the Central region of human CHRNA10. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于BIN1抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**: "BIN1 is a key regulator of proinflammatory and neurodegeneration-related activation in microglia"
**作者**: De Rossi P, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用BIN1抗体(Western blot和免疫荧光)揭示了BIN1蛋白在小胶质细胞炎症反应和神经退行过程中的调控作用,发现BIN1缺失会加剧神经炎症和神经元损伤。
2. **文献名称**: "Amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain-dependent regulation of BIN1 protein stability"
**作者**: Ubelmann F, et al.
**摘要**: 通过BIN1特异性抗体检测,研究发现阿尔茨海默病中β-淀粉样蛋白前体(APP)的胞内结构域与BIN1稳定性相关,BIN1异常聚集可能导致突触功能障碍。
3. **文献名称**: "BIN1 reverses PD-L1-mediated immune escape by inactivating the cGAS-STING pathway in triple-negative breast cancer"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献通过免疫共沉淀(使用BIN1抗体)证明BIN1通过抑制cGAS-STING信号通路增强肿瘤免疫应答,为BIN1抗体在癌症免疫治疗中的应用提供依据。
如需更多文献或具体研究领域,可进一步补充说明。
BIN1 (Bridging Integrator 1) is a ubiquitously expressed protein belonging to the BAR (Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs) domain-containing family, which plays critical roles in membrane remodeling, endocytosis, and cytoskeleton regulation. It is involved in diverse cellular processes, including vesicle trafficking, apoptosis, and cell differentiation. BIN1 has gained significant attention due to its association with multiple diseases. In cancer, BIN1 acts as a tumor suppressor in certain contexts but may exhibit oncogenic properties in others, depending on isoform expression and cellular context. Notably, BIN1 is a major genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, where it influences tau pathology and amyloid-β metabolism. It also links to cardiovascular diseases, particularly cardiac arrhythmias and myopathies, through its role in T-tubule formation in cardiomyocytes.
BIN1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions. Multiple isoforms generated by alternative splicing require isoform-specific antibodies for accurate detection. These antibodies enable applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry, helping researchers map BIN1's dynamic roles in health and disease. Additionally, they aid in investigating post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) that regulate BIN1 function. Validating antibody specificity is crucial due to BIN1's structural homology with other BAR proteins. High-quality BIN1 antibodies are vital for advancing research into its dual roles in neurodegeneration, cancer progression, and cardiac dysfunction, as well as its potential as a therapeutic target or diagnostic biomarker.
×