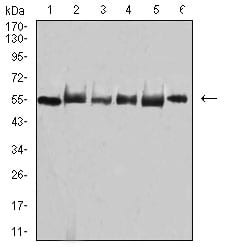
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
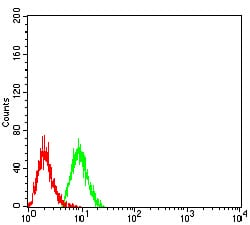
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
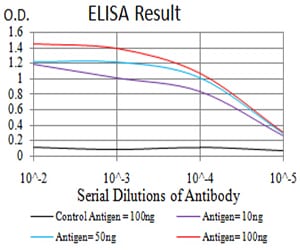
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TRAP; TRAP3; MGC:45012 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7186 |
| clone | 4A12D9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human TRAF2 (AA: 39-188) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TRAF2抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **"TRAF2 differentially regulates TNF-mediated NF-κB and JNK/AP-1 activation through interaction with cIAP1"**
*作者:Vince, J.E. 等*
**摘要**:该研究利用TRAF2抗体揭示TRAF2通过与cIAP1结合,在TNF信号通路中分别调控NF-κB的激活和JNK/AP-1通路的抑制,影响细胞存活与凋亡的平衡。
2. **"TRAF2 is required for TNFα-induced JNK but not NF-κB activation through a novel TRAF2-interacting protein"**
*作者:Yeh, W.C. 等*
**摘要**:通过TRAF2抗体的免疫共沉淀实验,发现TRAF2在TNFα信号中特异性激活JNK通路而非NF-κB,其功能依赖于与新型结合蛋白的相互作用,为炎症反应机制提供新见解。
3. **"TRAF2 suppresses basal IKK activity in resting cells to control basal NF-κB activity"**
*作者:Zheng, C. 等*
**摘要**:研究通过TRAF2抗体敲除实验证明,TRAF2在静息细胞中抑制IKK复合物活性,防止NF-κB的异常激活,维持免疫稳态,其缺失会导致自发性炎症反应。
4. **"Structural basis for the interaction of TRAF2 with the CD40 cytoplasmic domain"**
*作者:McWhirter, S.M. 等*
**摘要**:利用TRAF2抗体的结构生物学分析,解析了TRAF2与CD40受体胞内结构域结合的三维构象,阐明其在B细胞活化信号转导中的分子机制。
这些文献覆盖了TRAF2在信号转导、结构生物学及疾病调控中的关键作用,均通过TRAF2抗体进行功能或机制研究。
**Background of TRAF2 Antibody**
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) is an adaptor protein critical for regulating cellular signaling pathways, particularly those mediated by the TNF receptor superfamily and toll-like receptors (TLRs). TRAF2 plays a central role in NF-κB and MAPK signaling cascades, influencing processes such as cell survival, apoptosis, inflammation, and immune responses. It facilitates signal transduction by interacting with receptors (e.g., TNFR1/2) and downstream effectors, often through its C-terminal TRAF domain, while its N-terminal RING and zinc finger domains contribute to ubiquitination-mediated regulatory mechanisms.
TRAF2 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies, often generated in rabbits or mice (monoclonal or polyclonal), enable detection of TRAF2 via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation. Researchers use TRAF2-specific antibodies to explore its involvement in diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions, where TRAF2 dysregulation can alter cell death pathways or inflammatory responses. Additionally, TRAF2 antibodies help investigate its interactions with binding partners (e.g., cIAP1/2) and its role in ubiquitination-dependent signaling. Validated antibodies ensure specificity for accurate mechanistic studies, aiding in the development of therapeutic strategies targeting TRAF2-related pathways.
×