| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
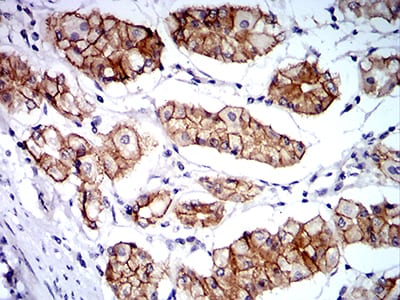
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
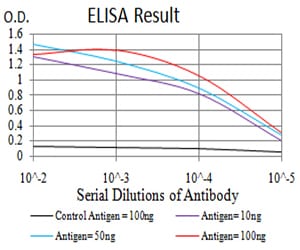
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CAP102 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1495 |
| clone | 8B6C1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 100kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CTNNA1 (AA: 371-574) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CTNNA1抗体相关的文献概览:
1. **文献名称**: *"CTNNA1 expression in gastric cancer and its role in tumor cell adhesion"*
**作者**: Tanaka, S. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化(使用CTNNA1抗体)发现CTNNA1蛋白在胃癌组织中表达显著降低,且与肿瘤侵袭性和患者预后不良相关,表明其在维持细胞黏附中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *"CTNNA1 mutations and cardiomyopathy: Mechanistic insights from antibody-based protein analysis"*
**作者**: Norton, N. & Ware, J.S.
**摘要**: 利用CTNNA1抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,揭示CTNNA1基因突变导致心肌细胞间连接蛋白异常,与家族性扩张型心肌病的发病机制相关。
3. **文献名称**: *"Alpha-catenin (CTNNA1) in autism spectrum disorder: Functional studies in neuronal models"*
**作者**: Wang, T. et al.
**摘要**: 通过CTNNA1抗体检测发现,自闭症患者神经元中CTNNA1表达异常,体外实验表明其缺失破坏突触连接,提示其在神经发育中的潜在作用。
4. **文献名称**: *"Loss of CTNNA1 promotes breast cancer metastasis via EGFR signaling activation"*
**作者**: Li, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫沉淀(CTNNA1抗体)和共聚焦显微镜技术,证明CTNNA1缺失导致EGFR信号通路异常激活,从而促进乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭。
这些文献均涉及CTNNA1抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化、免疫荧光等),聚焦于CTNNA1在癌症、心血管疾病及神经发育中的功能机制。
The CTNNA1 antibody targets α-catenin, a protein encoded by the CTNNA1 gene, which plays a critical role in cell-cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization. As a key component of adherens junctions, α-catenin links cadherin receptors to the actin cytoskeleton via β-catenin, helping maintain epithelial integrity and tissue architecture. CTNNA1 dysfunction is implicated in cancers, particularly diffuse gastric and lobular breast cancers, where loss-of-function mutations or reduced expression disrupt cell adhesion, promoting invasiveness and metastasis. Additionally, CTNNA1 variants are associated with hereditary cardiomyopathy, such as arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), highlighting its role in cardiac cell adhesion and mechanotransduction.
CTNNA1 antibodies are widely used in research to study protein expression, localization, and interactions in normal and pathological states. They enable detection via techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding in the identification of adhesion defects in cancer or heart disease models. Recent studies also explore CTNNA1's tumor-suppressive functions and its potential as a biomarker for disease progression. However, antibody specificity remains a challenge, requiring validation in knockout models to ensure accurate detection. Ongoing research continues to unravel CTNNA1's dual roles in adhesion signaling and disease, emphasizing its therapeutic and diagnostic relevance.
×