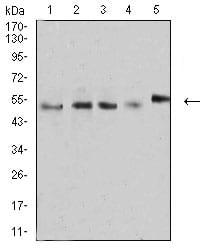
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
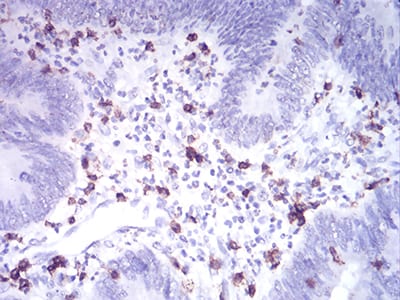
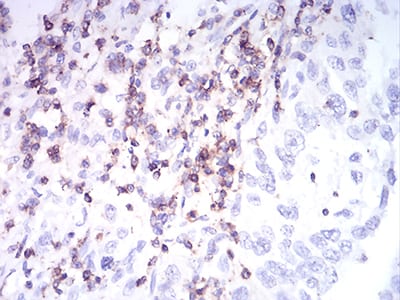
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
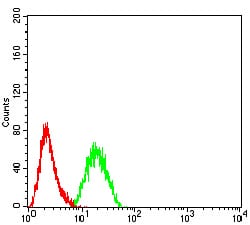
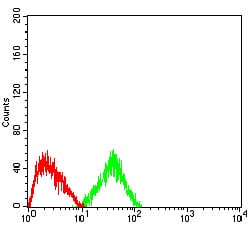
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
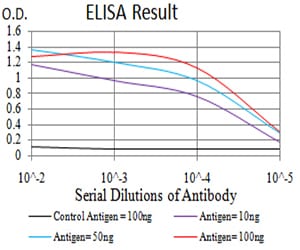
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T11; SRBC; LFA-2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 914 |
| clone | 3D1E3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD2 (AA: 25-140) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD2抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD2-mediated adhesion facilitates T lymphocyte antigen recognition function*
**作者**:Bierer BE, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了CD2分子在T细胞与抗原呈递细胞(APC)相互作用中的关键作用,发现抗CD2抗体可通过阻断CD2与配体LFA-3的结合,抑制T细胞受体(TCR)介导的抗原识别和信号传导,揭示了CD2在免疫突触形成中的辅助功能。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Prevention of graft-versus-host disease by anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody*
**作者**:Stuart JK, et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了一种抗CD2单克隆抗体(mAb)在移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)中的治疗效果。实验表明,该抗体通过靶向T细胞表面的CD2分子,显著抑制供体T细胞激活和增殖,延长了动物模型的生存期,提示其在临床移植中的潜在应用价值。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Functional characterization of anti-CD2 monoclonal antibodies: differential effects on T cell activation*
**作者**:Bolhuis RL, et al.
**摘要**:研究比较了不同克隆抗CD2单抗对T细胞功能的影响,发现部分抗体通过激活CD2信号通路增强T细胞增殖,而另一些则阻断CD2-LFA-3结合抑制T细胞应答,强调了CD2抗体功能的高度特异性及其在免疫调节中的双向作用。
---
如需扩展,可补充一篇综述:
4. **文献名称**:*CD2 as a therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases and transplantation*
**作者**:Trowbridge IS, Thomas ML
**摘要**:综述总结了CD2在T细胞介导的自身免疫病和移植排斥中的病理机制,并讨论了抗CD2抗体、融合蛋白等靶向策略的临床前及临床试验进展,强调其作为免疫干预靶点的潜力。
---
以上文献涵盖基础机制、治疗应用及抗体功能研究,可根据实际需求选择参考。
CD2 Antibody Background
CD2. also known as LFA-2 (lymphocyte function-associated antigen 2), is a 50-55 kDa cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is primarily expressed on T lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and thymocytes. Discovered in the early 1980s, CD2 plays a critical role in mediating cell-cell interactions in the immune system. Its primary ligand is LFA-3 (CD58) in humans and CD48 in rodents, facilitating adhesion between T cells and antigen-presenting cells (APCs) or target cells. This interaction is essential for T-cell activation, cytotoxicity, and immune synapse formation.
CD2 antibodies, such as OKT11 and Leu-5b, have been widely used in research and diagnostics. They are employed to study T-cell development, activation, and adhesion mechanisms. In flow cytometry, anti-CD2 antibodies help identify and isolate T-cell subsets. Functionally, some CD2 antibodies act as agonists or antagonists, modulating T-cell responses by either enhancing or blocking CD2-ligand interactions. Early studies revealed that CD2 signaling can synergize with T-cell receptor (TCR) signals to amplify activation or, in certain contexts, induce anergy.
Therapeutically, CD2-targeting strategies have been explored in autoimmune diseases and transplantation. For example, alefacept, a fusion protein targeting CD2. was once used to treat psoriasis by depleting pathogenic T cells. Despite its reduced clinical use today, CD2 remains a key molecule in understanding adaptive immunity and developing immunomodulatory therapies. Research continues to explore its role in infectious diseases, cancer immunotherapy, and immune regulation.
×