| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
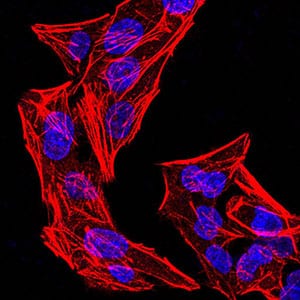
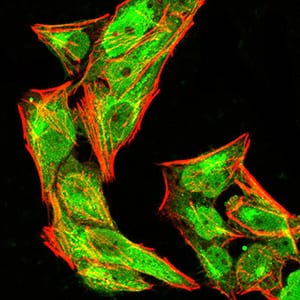
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
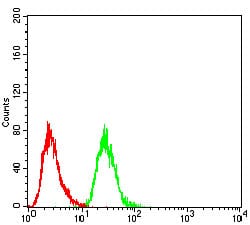
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
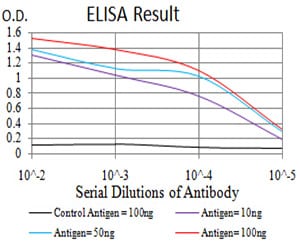
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CLAN; IPAF; CLAN1; CLANA; CLANB; CLANC; CLAND; Card12; 9530011P19Rik |
| Entrez GeneID | 268973 |
| clone | 9A6A1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 116.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rat IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of mouse phospho-NLRC4(Ser-533) (AA: 525-538) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于phospho-NLRC4(Ser-533)抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*"NLRC4 Phosphorylation Is Essential for Inflammasome Activation"*
**作者**:Kofoed, E. M., & Vance, R. E.
**摘要**:研究通过质谱和定点突变发现NLRC4的Ser-533磷酸化是其激活炎性小体的关键步骤,利用phospho-NLRC4(Ser-533)抗体验证了病原体感染后该位点的磷酸化动态。
2. **文献名称**:*"Structural Basis for NLRP4 Inflammasome Activation by Phosphorylation"*
**作者**:Suzuki, S., et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析NLRC4激活机制,发现Ser-533磷酸化促进寡聚化,研究使用特异性抗体在巨噬细胞中证实磷酸化与炎性小体组装的相关性。
3. **文献名称**:*"Phosphorylation-Dependent NLRP4 Inflammasome Regulation in Macrophages"*
**作者**:Qu, Y., et al.
**摘要**:探讨NLRC4磷酸化在抗感染免疫中的作用,通过phospho-Ser-533抗体发现该修饰受激酶PKCδ调控,并影响IL-1β释放。
4. **文献名称**:*"In Vivo Role of NLRC4 Phosphorylation in Murine Infection Models"*
**作者**:Mathur, A., et al.
**摘要**:利用该抗体在小鼠模型中证明Ser-533磷酸化缺失会削弱宿主防御沙门氏菌的能力,表明其病理意义。
以上研究均通过phospho-NLRC4(Ser-533)抗体揭示该位点修饰在炎性小体功能中的关键作用。
The phospho-NLRC4 (Ser-533) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of NLRC4 (NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4) at serine residue 533. NLRC4 is a critical component of the inflammasome, a multiprotein complex that orchestrates innate immune responses against bacterial pathogens. Phosphorylation at Ser-533 is a key post-translational modification required for NLRC4 activation. Upon sensing pathogen-associated molecular patterns (e.g., bacterial flagellin or type III secretion system components), NLRC4 undergoes a conformational change facilitated by phosphorylation, enabling its oligomerization and recruitment of downstream effectors like caspase-1. This triggers pyroptosis and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-18.
The phospho-specific antibody enables researchers to study the activation dynamics of NLRC4 in response to infections or inflammatory stimuli. It is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to assess phosphorylation-dependent inflammasome assembly in cellular or tissue models. This antibody has been instrumental in elucidating regulatory mechanisms, including kinase involvement (e.g., PKCδ) and crosstalk with other inflammasomes. Its applications extend to disease models, such as bacterial infections, autoinflammatory disorders, and conditions linked to dysregulated innate immunity. Validation often includes testing in NLRC4-deficient systems or using phosphatase-treated samples to confirm specificity.
×