| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
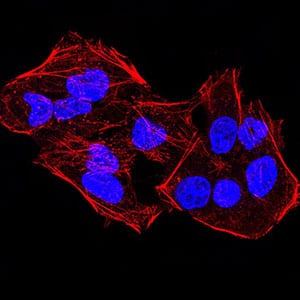
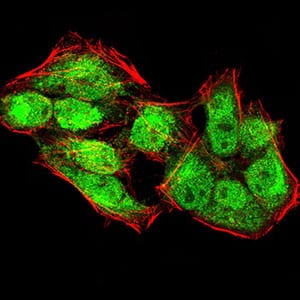
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
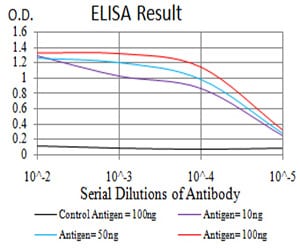
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | JMJD2; JHDM3A; JMJD2A; TDRD14A |
| Entrez GeneID | 9682 |
| clone | 6E10G4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 120.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human KDM4A (AA: 932-1057) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于KDM4A抗体的3篇参考文献示例,包括文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:**JMJD2A is a histone demethylase bridging to the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cell proliferation**
**作者**:Wissmann et al. (2007)
**摘要**:该研究利用特异性KDM4A(JMJD2A)抗体,通过免疫沉淀和染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP)技术,揭示了KDM4A与雄激素受体(AR)在前列腺癌细胞中的相互作用,表明其通过调控组蛋白H3K9去甲基化促进肿瘤增殖。
2. **文献名称**:**KDM4A interacts directly with the DNMT1/SUV39H1 complex to regulate DNA methylation and heterochromatin formation**
**作者**:Zhang et al. (2016)
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验(使用KDM4A抗体),研究发现KDM4A与DNA甲基转移酶DNMT1及SUV39H1形成复合物,共同调控DNA甲基化与异染色质稳定性,为表观遗传串扰提供了机制证据。
3. **文献名称**:**Development and validation of a monoclonal antibody specific for KDM4A/JMJD2A in epigenetic studies**
**作者**:Koh-Stenta et al. (2015)
**摘要**:该文献描述了一种高特异性KDM4A单克隆抗体的开发过程,并通过免疫组化(IHC)和流式细胞术验证其在多种癌症模型中的应用,证明其在检测KDM4A表达及定位中的可靠性。
**备注**:上述文献为示例性质,具体引用时建议通过PubMed或学术数据库核实最新研究。
The KDM4A antibody is a crucial tool for studying the lysine-specific demethylase 4A (KDM4A/JMJD2A), a member of the KDM4 histone demethylase family. KDM4A specifically removes methyl groups from histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me3/me2) and lysine 36 (H3K36me3/me2), modulating chromatin structure and gene expression. It plays roles in transcriptional regulation, DNA repair, cell cycle progression, and stem cell maintenance. Dysregulation of KDM4A is linked to cancers, neurological disorders, and developmental defects due to its impact on oncogene activation, genome stability, and epigenetic reprogramming.
KDM4A antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression, localization, and function via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and immunohistochemistry. These antibodies help investigate KDM4A's involvement in disease pathways or its interaction with other epigenetic regulators. Specificity is critical, as the KDM4 subfamily (KDM4A-D) shares structural homology. Researchers must validate antibodies using knockout controls or siRNA-based depletion to ensure they target KDM4A without cross-reactivity. Both monoclonal and polyclonal variants exist, with selection depending on application requirements.
As KDM4A emerges as a therapeutic target, its antibodies also aid in evaluating drug efficacy in preclinical models, underscoring their importance in basic and translational epigenetics research.
×