
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
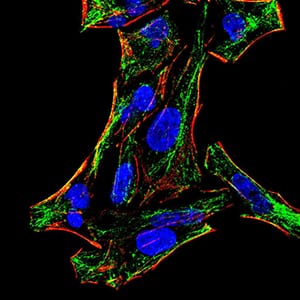
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
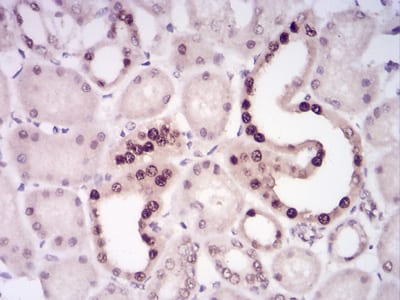
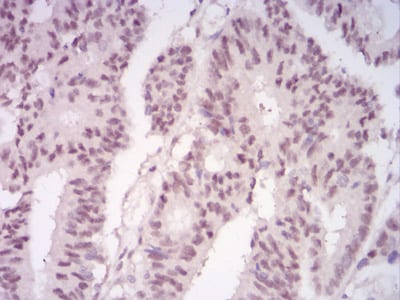
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APR; LRP; A2MR; CD91; APOER; LRP1A; TGFBR5; IGFBP3R |
| Entrez GeneID | 4035 |
| clone | 1C8G6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 504kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LRP1 (AA: 20-155) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于LRP1抗体的代表性文献摘要概括(基于公开研究内容整理):
---
1. **文献名称**:*LRP1 in Neurological and Cardiovascular Disorders*
**作者**:Bu G, et al.
**摘要**:探讨LRP1在阿尔茨海默病中的角色,使用特异性抗体发现其参与β-淀粉样蛋白清除,提示靶向LRP1的抗体可能具有治疗潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Antibody-mediated LRP1 Blockade Enhances CNS Lymphocyte Entry*
**作者**:Giles DA, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗LRP1抗体抑制其功能,证明LRP1调控血脑屏障通透性,为多发性硬化等神经炎症疾病提供治疗新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*LRP1 Modulates Tumor Cell Invasion via EGFR Signaling*
**作者**:Meng H, et al.
**摘要**:使用抗LRP1抗体揭示其在癌细胞侵袭中的双重作用,发现LRP1与EGFR相互作用促进肿瘤转移,提示其作为癌症治疗靶点。
---
4. **文献名称**:*LRP1 Antibody Characterization for Atherosclerosis Research*
**作者**:Muratoglu SC, et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型抗LRP1单克隆抗体的开发,验证其结合特异性并应用于动脉粥样硬化模型中血管平滑肌细胞功能研究。
---
注:以上内容为文献核心发现的概括,非原文摘要。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索标题/作者获取原文。
LRP1 (LDL receptor-related protein 1), also known as CD91 or α-2-macroglobulin receptor, is a multifunctional transmembrane receptor belonging to the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family. It plays critical roles in endocytosis, cell signaling, and maintaining cellular homeostasis by interacting with diverse ligands, including apolipoprotein E, proteases, extracellular matrix proteins, and pathogen-derived molecules. LRP1 is ubiquitously expressed, with high levels in the liver, brain, vascular smooth muscle cells, and macrophages. Its involvement in lipid metabolism, neuronal survival, and clearance of amyloid-β has linked it to Alzheimer’s disease, atherosclerosis, and cancer metastasis.
LRP1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its structure, function, and tissue distribution. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to detect LRP1 expression and localization. Specific monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies targeting extracellular or intracellular domains help elucidate LRP1’s dual role in ligand internalization and signal transduction. Recent research also explores therapeutic applications, such as modulating LRP1 activity to influence amyloid-β clearance in Alzheimer’s or inhibit tumor invasion. However, challenges remain in distinguishing LRP1 from homologous receptors and characterizing its splice variants. Validating antibody specificity through knockout controls remains crucial for accurate experimental interpretation.
×