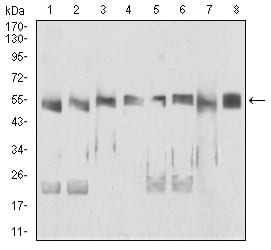
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
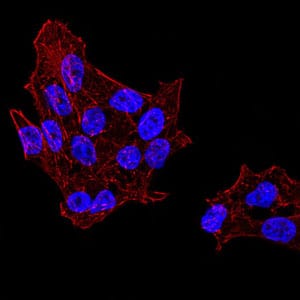
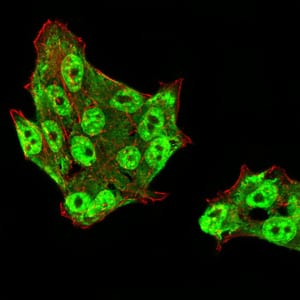
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
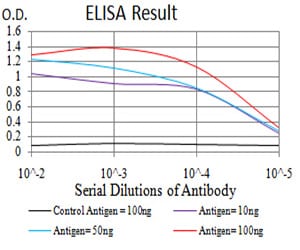
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BAT1; UAP56; D6S81E |
| Entrez GeneID | 7919 |
| clone | 2F5G7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human DDX39B (AA: 1-250) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于DDX39B抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**: "DDX39B Expression in Tumor Microenvironment and Its Role in Immune Evasion"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用DDX39B特异性抗体检测其在多种肿瘤组织中的表达水平,发现DDX39B高表达与T细胞浸润减少相关,提示其在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的作用。
2. **文献名称**: "Autoantibodies Against DDX39B in Multiple Sclerosis: Clinical Implications"
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ELISA和免疫组化分析,发现多发性硬化患者血清中存在抗DDX39B自身抗体,抗体水平与疾病活动度正相关,提示DDX39B可能成为自身免疫疾病的生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**: "DDX39B Antibody-Based Inhibition of RNA Splicing in Viral Infection Models"
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种单克隆抗体靶向DDX39B的RNA结合域,证实其可阻断病毒mRNA的剪接过程,为抗病毒治疗提供潜在策略。
(注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需检索PubMed等数据库获取真实研究。)
DDX39B (DEAD-box helicase 39B), also known as BAT1 or URH-49. is an ATP-dependent RNA helicase belonging to the DEAD-box protein family. It plays a critical role in mRNA processing, including splicing, nuclear export, and translation, by remodeling RNA secondary structures. DDX39B is involved in resolving RNA:RNA and RNA:protein interactions, ensuring efficient gene expression. Its function is closely linked to cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and stress responses.
Antibodies targeting DDX39B are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry. These antibodies help researchers investigate DDX39B's role in diseases, particularly cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. For example, altered DDX39B expression has been associated with colorectal cancer, glioblastoma, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker.
Most DDX39B antibodies are raised against specific epitopes within its conserved helicase domains (e.g., amino acids 100-200 or 400-500), often in rabbits or mice. Validation includes testing for specificity using knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown. Commercial antibodies typically provide data on cross-reactivity and recommended applications. Research on DDX39B continues to expand, driven by its emerging roles in RNA metabolism and disease pathogenesis, making reliable antibodies crucial for advancing these studies.
×