| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
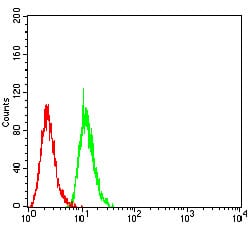
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
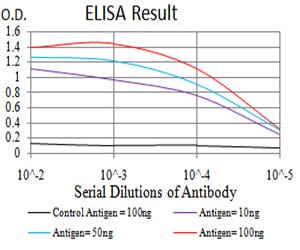
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIR2L7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 51547 |
| clone | 1E2B2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human SIRT7 (AA: 1-105) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于SIRT7抗体的参考文献摘要(文献名称、作者及核心内容概括):
---
1. **文献名称**:*SIRT7 links H3K18 deacetylation to maintenance of oncogenic transformation*
**作者**:Barber et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了SIRT7通过特异性去乙酰化组蛋白H3K18.维持癌细胞转化能力。研究中利用SIRT7抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫印迹(WB),证实SIRT7缺失导致H3K18乙酰化水平升高,抑制肿瘤生长。
---
2. **文献名称**:*SIRT7 suppresses aging-associated cardiac hypertrophy through regulation of autophagy*
**作者**:Shin et al.
**摘要**:通过SIRT7基因敲除小鼠模型,研究证明SIRT7通过调控自噬途径延缓心脏衰老。使用SIRT7抗体进行免疫组化(IHC)和免疫荧光(IF),发现SIRT7缺失导致心肌细胞自噬失调和病理性肥大。
---
3. **文献名称**:*SIRT7-dependent deacetylation of CDK9 activates RNA polymerase II transcription*
**作者**:Li et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道SIRT7通过去乙酰化CDK9激酶,调控RNA聚合酶II的转录活性。研究通过SIRT7抗体进行共免疫沉淀(Co-IP)和蛋白质互作分析,揭示其在转录延伸中的关键作用。
---
如需具体实验细节或扩展文献范围,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“SIRT7 antibody”为关键词进一步筛选。
SIRT7 is a member of the sirtuin family of NAD⁺-dependent protein deacetylases, which play roles in chromatin modification, genome stability, and metabolic regulation. Specifically, SIRT7 is localized to the nucleolus and is highly expressed in metabolically active tissues such as the liver and heart. It is implicated in regulating ribosomal DNA (rDNA) transcription, DNA damage repair, and cellular stress responses. SIRT7’s enzymatic activity has been linked to aging, cancer, and metabolic disorders, with studies showing its overexpression in certain cancers (e.g., breast, liver) and its role in promoting tumorigenesis through epigenetic modulation.
SIRT7 antibodies are essential tools for investigating its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are typically generated using immunogenic peptides or recombinant SIRT7 protein fragments as antigens, often in hosts like rabbits or mice. Validated antibodies enable applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation. However, specificity remains a critical consideration due to potential cross-reactivity with other sirtuin family members (e.g., SIRT1 or SIRT6). Researchers frequently validate SIRT7 antibodies using knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown to confirm target specificity. Commercial antibodies often provide data on species reactivity, post-translational modification detection, and recommended experimental conditions. Recent studies employing SIRT7 antibodies have clarified its role in nucleolar stress responses, lipid metabolism, and interactions with non-coding RNAs, underscoring its therapeutic potential in age-related diseases and cancer.
×