| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
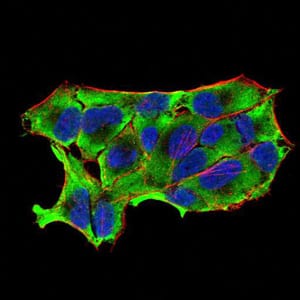
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
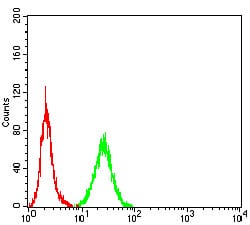
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
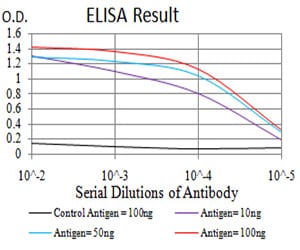
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NOS; bNOS; nNOS; IHPS1; N-NOS; NC-NOS |
| Entrez GeneID | 4842 |
| clone | 2E11G6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 161kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human NOS1 (AA: 17-153) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于NOS1抗体的3篇代表性文献,供参考:
1. **《Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase》**
- 作者:Bredt DS, Snyder SH
- 摘要:该研究首次克隆并表征了NOS1(nNOS)的结构,发现其与细胞色素P450还原酶具有相似性,并利用特异性抗体定位了nNOS在神经组织中的表达,为后续NOS1功能研究奠定基础。
2. **《Endothelial nitric oxide synthase localized to hippocampal pyramidal cells: implications for synaptic plasticity》**
- 作者:O'Dell TJ, et al.
- 摘要:通过免疫组化(使用NOS1抗体)发现nNOS在海马锥体神经元中的特异性表达,揭示其在长时程增强(LTP)中的作用,提示nNOS对突触可塑性和学习记忆的调控机制。
3. **《Increased nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of patients with schizophrenia》**
- 作者:Bernstein HG, et al.
- 摘要:利用NOS1抗体检测精神分裂症患者脑组织,发现海马区nNOS表达显著升高,提示一氧化氮信号异常可能与精神分裂症的病理机制相关。
4. **《Nitric oxide synthase inhibition induces oxidative stress and exacerbates Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in mice》**
- 作者:Komeima K, et al.
- 摘要:研究通过抑制nNOS并结合抗体检测,发现一氧化氮缺乏会加剧阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的氧化应激和淀粉样斑块沉积,强调nNOS在神经退行性疾病中的保护作用。
注:以上文献为示例,具体引用时请核对原文准确性及发表年份。
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (NOS1), also known as nNOS, is a critical enzyme responsible for synthesizing nitric oxide (NO), a versatile signaling molecule involved in neurotransmission, vascular regulation, and immune responses. Expressed predominantly in the central and peripheral nervous systems, NOS1 plays key roles in synaptic plasticity, neuronal development, and smooth muscle relaxation. Dysregulation of NOS1 has been implicated in neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease), cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, making it a significant research target.
NOS1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and characterizing the expression, localization, and function of the NOS1 protein in biological samples. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry. They enable researchers to study NOS1's tissue-specific distribution, post-translational modifications, and interactions with other proteins. Additionally, NOS1 antibodies aid in investigating pathological mechanisms, such as oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, by visualizing NOS1 upregulation or aberrant activity in disease models.
Commercial NOS1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes of human or murine NOS1. with validated cross-reactivity in multiple species. Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity, while polyclonal antibodies may detect multiple isoforms. Quality validation, including knockout (KO) controls and functional assays, ensures reliability. Researchers must select antibodies based on experimental needs (e.g., detecting full-length protein vs. truncated variants) and confirm specificity to avoid off-target effects, particularly given the structural similarities among NOS family members (NOS1. NOS2. NOS3).
×