

| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
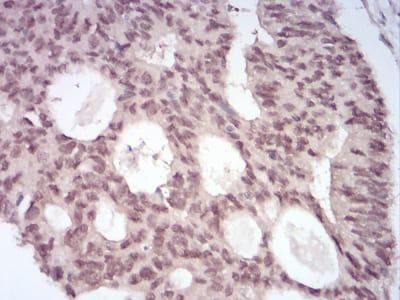
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
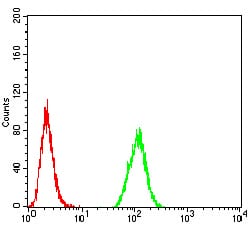
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
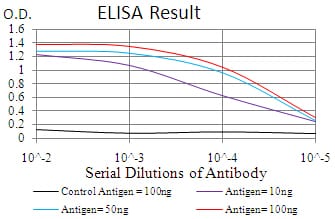
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EC 2.1.1.63 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4255 |
| clone | 1A11F8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MGMT (AA: 32-210) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于MGMT抗体的代表性文献摘要,按发表时间排序:
---
1. **文献名称**:*MGMT Gene Silencing and Benefit from Temozolomide in Glioblastoma*
**作者**:Esteller, M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次证明MGMT启动子甲基化导致基因沉默,并与胶质母细胞瘤患者对烷化剂化疗(如替莫唑胺)的敏感性显著相关,提示MGMT蛋白低表达可作为预后标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*MGMT Promoter Methylation in Malignant Gliomas: Therapeutic Ready?*
**作者**:Hegi, M.E., et al.
**摘要**:通过多中心临床数据分析,证实MGMT启动子甲基化状态是预测胶质瘤患者接受替莫唑胺治疗后生存期延长的独立指标,并讨论了基于抗体的免疫组化(IHC)检测与甲基化特异性PCR(MSP)方法的一致性争议。
3. **文献名称**:*Assessment of MGMT Status in Glioblastoma: Pitfalls and Recommendations*
**作者**:Preusser, M., et al.
**摘要**:系统比较了IHC(使用抗MGMT抗体)与分子检测方法(如甲基化分析)在评估MGMT状态中的优缺点,指出IHC可能存在假阳性/阴性问题,建议结合多种方法提高临床可靠性。
4. **文献名称**:*O⁶-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase (MGMT) in Human Cancer: A Systematic Review*
**作者**:Weller, M., et al.
**摘要**:综述了MGMT在不同癌症(尤其是胶质瘤)中的生物学功能、检测方法(包括抗体技术)及其在个性化治疗中的临床应用,强调标准化检测流程的重要性。
---
**注**:以上文献多发表于《New England Journal of Medicine》《Acta Neuropathologica》等权威期刊,具体年份可补充(如Esteller, 2000;Hegi, 2005;Preusser, 2008;Weller, 2010)。如需完整引用格式或更多文献,可进一步说明。
MGMT (O⁶-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase) is a DNA repair enzyme that plays a critical role in maintaining genomic integrity by removing alkyl groups from the O⁶ position of guanine, a common site of DNA damage induced by alkylating chemotherapeutic agents like temozolomide. In cancer biology, MGMT expression is inversely associated with treatment response; high MGMT activity can counteract the cytotoxic effects of alkylating drugs by repairing DNA damage, thereby conferring tumor resistance.
Epigenetic silencing of the *MGMT* gene via promoter methylation is a key mechanism leading to reduced enzyme expression. This methylation status has emerged as a predictive biomarker in glioblastoma (GBM), where methylated *MGMT* promoters correlate with improved survival in patients treated with temozolomide and radiotherapy.
MGMT antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to detect protein expression in tumor tissues. However, IHC results may not always align with methylation assays (e.g., methylation-specific PCR or pyrosequencing) due to post-transcriptional regulation or technical variability. Despite this, IHC remains a practical tool for assessing MGMT protein levels in resource-limited settings.
Clinical guidelines increasingly prioritize molecular testing for methylation status, but MGMT antibodies retain utility in research and diagnostic workflows to explore protein expression patterns and validate epigenetic findings. Their application underscores the importance of MGMT as a therapeutic biomarker in tailoring alkylating chemotherapy for cancers, particularly gliomas.
×