| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
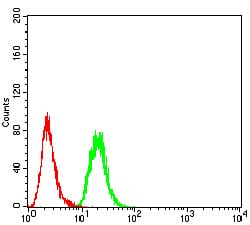
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
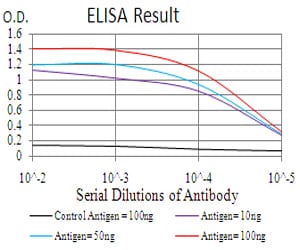
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CT31; PLU1; PUT1; PLU-1; JARID1B; PPP1R98; RBBP2H1A |
| Entrez GeneID | 10765 |
| clone | 7H3D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 175.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human KDM5B (AA: 231-319) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于KDM5B抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容的简要概括:
---
1. **"KDM5B promotes breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis through regulation of E-cadherin expression"**
*作者:Yamane K et al.*
**摘要**:该研究利用KDM5B抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现KDM5B通过去甲基化组蛋白H3K4me3抑制E-钙粘蛋白表达,从而促进乳腺癌细胞侵袭和转移,并与患者预后不良相关。
2. **"Targeting KDM5B in cancer therapy: a novel epigenetic approach"**
*作者:Yang GJ et al.*
**摘要**:研究通过KDM5B抗体验证其在小细胞肺癌中的高表达,并开发了靶向KDM5B的小分子抑制剂,证明其可恢复肿瘤抑制基因表达并抑制肿瘤生长。
3. **"KDM5B regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation through modulating histone methylation"**
*作者:Christensen J et al.*
**摘要**:使用KDM5B抗体进行ChIP-seq分析,揭示KDM5B通过调控多能性基因区域的H3K4me3水平,维持胚胎干细胞自我更新并影响分化进程。
---
以上文献展示了KDM5B抗体在疾病机制研究、治疗靶点开发及表观遗传调控分析中的具体应用。如需补充更多研究或调整方向,请随时提出。
KDM5B (lysine-specific demethylase 5B), also known as JARID1B or PLU-1. is a member of the KDM5 family of histone demethylases that specifically catalyze the removal of methyl groups from di- and tri-methylated lysine 4 on histone H3 (H3K4me2/me3), a chromatin mark associated with active transcription. By modulating H3K4 methylation states, KDM5B plays a critical role in regulating gene expression, cellular differentiation, and epigenetic memory. It contains conserved structural domains, including the JmjC domain responsible for its enzymatic activity.
Dysregulation of KDM5B is linked to cancer progression, stem cell maintenance, and drug resistance. Overexpression of KDM5B has been observed in various cancers (e.g., breast cancer, melanoma, lung cancer), where it suppresses tumor suppressor genes and promotes oncogenic pathways. This enzyme is also implicated in maintaining cancer stem cell populations, contributing to tumor recurrence and therapy resistance.
KDM5B antibodies are essential tools in research for detecting protein expression, localization, and interaction partners via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). They enable studies exploring KDM5B's role in epigenetic regulation, cancer biology, and response to therapeutic inhibitors targeting its demethylase activity. Validated antibodies are critical for ensuring specificity, given the high homology among KDM5 family members. Research on KDM5B continues to advance understanding of epigenetic mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies in oncology.
×