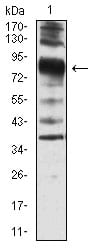
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
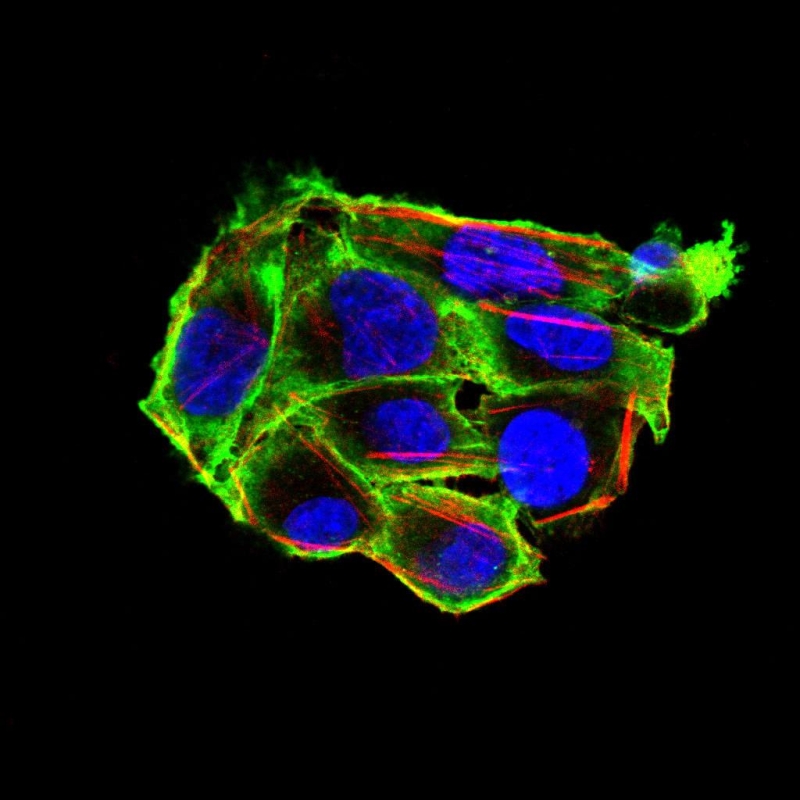
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
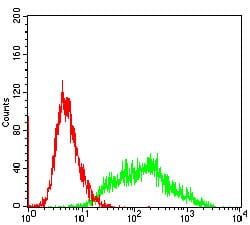
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
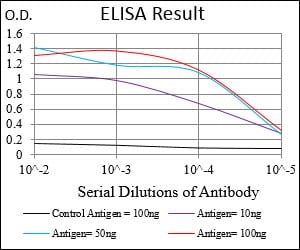
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VIL; D2S1471 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7429 |
| clone | 3E5G11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 92.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human VIL1 (AA: 1-209) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与VIL1(Villin-1)抗体相关的文献摘要信息:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Villin-1 is a marker for gastric adenocarcinoma with intestinal differentiation*
**作者**:Wang, K., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化分析发现,VIL1抗体在肠型胃癌中特异性高表达,可作为区分肠型与弥漫型胃癌的分子标志物,对临床病理分型具有辅助诊断价值。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Role of Villin in the maintenance of intestinal epithelial barrier function*
**作者**:Cheng, H., et al.
**摘要**:文章利用VIL1抗体敲除模型,证明Villin-1蛋白通过调控微丝重组维持肠道上皮屏障完整性,其缺失会导致细胞间连接破坏和炎症反应加剧。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Villin immunohistochemistry is a reliable marker for microvillus inclusion disease*
**作者**:Müller, T., et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,VIL1抗体在微绒毛包涵体病(MVID)患者的肠活检组织中呈现异常胞质聚集,可作为该罕见遗传病的特异性病理诊断指标。
---
这些文献展示了VIL1抗体在肿瘤分型、肠道屏障功能研究和遗传病诊断中的关键作用。如需具体文献链接或更多信息,可进一步提供数据库检索支持。
The Villin-1 (VIL1) antibody is a valuable tool in biomedical research and diagnostics, targeting the Villin-1 protein, a member of the gelsolin family of actin-binding proteins. Villin-1 is primarily expressed in epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract, kidney, and liver, where it plays a critical role in maintaining cell structure and function. It is localized to the brush border of absorptive epithelial cells, such as enterocytes, and is involved in actin filament reorganization, microvilli formation, and cell motility. Its expression is tightly regulated during development and differentiation, making it a marker for polarized epithelial cells.
VIL1 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blotting to study epithelial cell differentiation, tissue-specific protein localization, and pathological conditions like colorectal cancer, where Villin-1 overexpression is observed. In clinical diagnostics, VIL1 antibodies aid in identifying tumors of gastrointestinal origin, helping differentiate primary adenocarcinomas from metastatic cancers. Additionally, Villin-1's role in intestinal barrier function links it to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), where its expression may correlate with disease progression.
Produced in hosts like rabbits or mice, VIL1 antibodies are validated for specificity and sensitivity across applications. Their utility extends to investigating epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer and evaluating gut integrity in experimental models. Overall, VIL1 antibodies serve as essential reagents for understanding epithelial biology and disease mechanisms.
×