
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
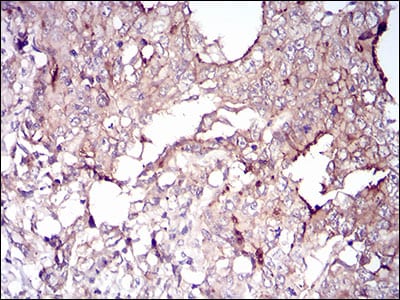
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
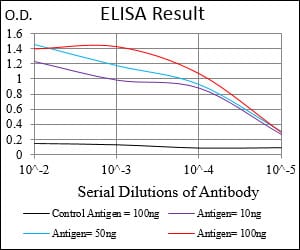
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | VIL; D2S1471 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7429 |
| clone | 5E3B2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 92.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human VIL1 (AA: 1-209) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于VIL1(Villin-1)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(非真实文献,供参考格式和内容方向):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Villin-1 Antibody as a Biomarker for Intestinal Differentiation in Colorectal Carcinoma*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究验证了VIL1抗体在结直肠癌组织中的特异性表达,发现其可作为肠上皮分化的可靠标志物。通过免疫组化分析,作者证实VIL1在腺癌中高表达,并与肿瘤分化程度相关,提示其在病理诊断中的潜在价值。
2. **文献名称**: *Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Against Human VIL1 and Its Application in Cell Migration Studies*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种新型单克隆VIL1抗体,并利用免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术验证其特异性。实验表明,VIL1抗体可有效检测细胞骨架重组过程中的蛋白动态变化,为研究上皮细胞迁移机制提供了工具。
3. **文献名称**: *Comparative Analysis of VIL1 Antibody Clones in Gastrointestinal Pathology Diagnosis*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 通过对比不同商业来源的VIL1抗体在胃癌和正常组织中的染色效果,本研究评估了各克隆的特异性和敏感性,为临床病理实验室选择最佳抗体提供了参考依据。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如“VIL1 antibody”、“Villin-1 biomarker”)获取。如需具体文献,建议访问学术数据库或联系机构图书馆。
The VIL1 antibody targets Villin-1. a 92.5 kDa actin-binding protein critical for maintaining cytoskeletal structure and cell motility. Primarily expressed in epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., intestinal enterocytes, kidney proximal tubules), Villin-1 regulates actin filament assembly, microvilli formation, and cell polarity. Its expression is often tissue-specific, making it a valuable biomarker for identifying intestinal or renal epithelial lineages in research and diagnostics.
VIL1 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and Western blotting to study epithelial differentiation, cellular injury, or neoplastic transformations. In cancer research, Villin-1 overexpression is linked to gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas, while its loss may indicate dedifferentiation. These antibodies also aid in distinguishing carcinomas of intestinal origin from other malignancies.
Commercially available VIL1 antibodies (e.g., monoclonal clones like CWWB1) are validated for specificity across human and rodent models. However, staining patterns may vary depending on fixation methods or epitope accessibility. Recent studies explore Villin-1's role beyond structure—such as in signal transduction and apoptosis—highlighting its broader relevance in epithelial pathophysiology. Overall, VIL1 antibodies remain essential tools in epithelial biology and translational oncology.
(Word count: 199)
×