| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
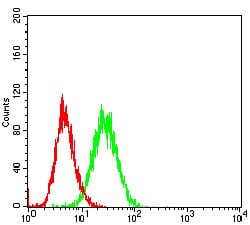
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
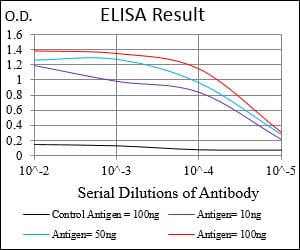
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FAT; GP4; GP3B; GPIV; CHDS7; PASIV; SCARB3; BDPLT10 |
| Entrez GeneID | 948 |
| clone | 5B6B2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 53kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD36 (AA: 30-130) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD36抗体的文献摘要概括,供参考:
1. **文献名称**: *CD36 antibodies induce thrombocytopenia and impair endothelial cell function in vitro*
**作者**: Ghosh A. et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨了抗CD36抗体在免疫性血小板减少症中的作用,发现特定CD36抗体可通过结合血小板和内皮细胞表面受体,导致血小板清除增加并引发内皮细胞炎症反应。
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting CD36 as a therapeutic strategy against cancer metastasis*
**作者**: Pascual G. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究揭示了CD36在肿瘤细胞脂质代谢和转移中的关键作用,并开发了一种人源化CD36单克隆抗体,实验显示其可阻断脂肪酸摄取,显著抑制小鼠模型中肿瘤转移。
3. **文献名称**: *Anti-CD36 antibodies in malaria: from immune response to pathogenesis*
**作者**: Urban B.C. et al.
**摘要**: 分析了疟疾感染中宿主产生的抗CD36自身抗体对疾病进程的影响,发现此类抗体可能通过干扰红细胞与内皮细胞的黏附,加重微血管阻塞和炎症反应。
4. **文献名称**: *CD36-dependent signaling mediates fatty acid-induced autophagy in endothelial cells*
**作者**: Li Y. et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现CD36抗体可抑制脂肪酸诱导的内皮细胞自噬过程,揭示了CD36在代谢应激下调控血管稳态的机制,为动脉粥样硬化治疗提供新靶点。
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar输入标题进一步获取全文细节。
CD36 antibodies are immunological tools targeting the CD36 glycoprotein, a class B scavenger receptor widely expressed on cell membranes, including macrophages, platelets, adipocytes, and endothelial cells. CD36 plays multifaceted roles in lipid metabolism, inflammation, angiogenesis, and pathogen recognition. It facilitates cellular uptake of long-chain fatty acids, oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDL), and phospholipids, contributing to metabolic regulation and atherosclerotic plaque formation. Additionally, CD36 mediates immune responses by interacting with pathogen-associated molecular patterns (e.g., malaria-infected erythrocytes) and modulating Toll-like receptor signaling.
CD36 antibodies are employed in research to detect CD36 expression, assess its function, or block ligand interactions. Monoclonal and polyclonal variants are used in techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting. Dysregulated CD36 expression is linked to metabolic disorders (e.g., insulin resistance), cardiovascular diseases, and cancer metastasis. Certain CD36 antibodies inhibit fatty acid uptake or oxLDL internalization, aiding mechanistic studies in metabolic syndromes. Clinically, CD36 deficiency (e.g., platelet glycoprotein IV deficiency) is diagnosed using specific antibodies. Challenges include variable antibody specificity due to CD36’s post-translational modifications. Ongoing studies explore therapeutic applications, such as targeting CD36 in obesity or tumor microenvironments. Overall, these antibodies are pivotal in elucidating CD36’s pathophysiological roles and translational potential.
×