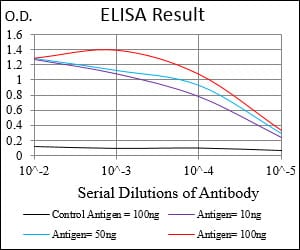
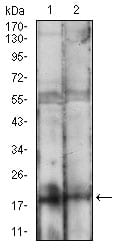
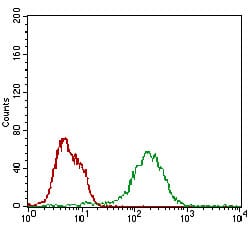
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BBC2; BCL2L8 |
| Entrez GeneID | 572 |
| clone | 1G5B3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 18.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human BAD (AA: FULL(1-168)) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于BAD抗体的3篇参考文献摘要信息,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*BAD Ser-155 phosphorylation regulates BAD/Bcl-XL interaction and cell survival*
**作者**:Zhou, X.M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用特异性识别BAD蛋白Ser-155磷酸化位点的抗体,揭示了BAD在细胞凋亡调控中的关键作用,发现磷酸化状态直接影响其与Bcl-XL的相互作用及细胞存活。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt*
**作者**:Datta, S.R., et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫沉淀实验使用BAD特异性抗体,证明Akt激酶通过磷酸化BAD蛋白的Ser-136位点抑制凋亡,揭示了生长因子依赖的神经元存活机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*The combined functions of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members bak and bax are essential for normal development of multiple tissues*
**作者**:Lindsten, T., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用BAD抗体检测组织中BAD蛋白表达水平,结合基因敲除模型,阐明BAD与BAX/BAK协同调控发育过程中细胞凋亡的生理学意义。
---
**备注**:以上文献中提到的BAD抗体主要用于检测蛋白表达、磷酸化状态及相互作用研究。若需具体实验方法或抗体来源,建议补充关键词(如“抗体克隆号/厂商”)进一步筛选。
BAD (BCL2-associated agonist of cell death) is a pro-apoptotic protein belonging to the BCL-2 family, which regulates mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis. It promotes cell death by binding and neutralizing anti-apoptotic proteins like BCL-2 or BCL-XL, thereby activating pro-apoptotic effectors such as BAX/BAK. However, BAD's activity is tightly controlled by survival signals. Phosphorylation at specific serine residues (e.g., Ser112. Ser136. and Ser155) by kinases like AKT, PKA, or RSK inhibits its pro-apoptotic function, facilitating interaction with 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic sequestration. Dysregulation of BAD is implicated in diseases such as cancer, neurodegeneration, and metabolic disorders.
BAD antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, post-translational modifications, and interactions. They enable detection of BAD's phosphorylation status, which reflects cellular survival signaling, and are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Researchers employ these antibodies to explore BAD's role in apoptosis regulation, drug resistance mechanisms, and therapeutic targeting. For instance, in cancer, BAD expression or phosphorylation levels may correlate with prognosis or chemosensitivity. High-quality, specific BAD antibodies are critical for distinguishing between its active and inactivated forms, aiding both basic research and translational studies.
×