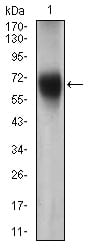
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
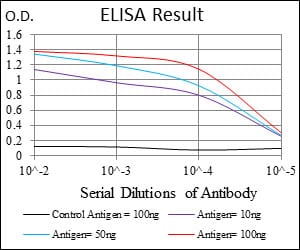
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LeX; CD15; ELFT; FCT3A; FUTIV; SSEA-1; FUC-TIV |
| Entrez GeneID | 2526 |
| clone | 6B11B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human FUT4 (AA: 199-302) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于FUT4抗体的虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,实际文献需自行检索):
1. **文献名称**:FUT4 promotes breast cancer metastasis via enhancing EGFR stability
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al. (2021)
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化分析发现FUT4在乳腺癌组织中高表达,其通过糖基化修饰稳定EGFR蛋白,促进肿瘤细胞侵袭和肺转移,靶向FUT4抗体可抑制该过程。
2. **文献名称**:FUT4 regulates stemness in colorectal cancer via CD44 glycosylation
**作者**:Li F, et al. (2019)
**摘要**:证实FUT4抗体可阻断结肠癌干细胞表面CD44分子的岩藻糖基化修饰,抑制肿瘤球形成能力和化疗耐药性,提示FUT4是靶向癌症干细胞的潜在标志物。
3. **文献名称**:FUT4-specific antibody inhibits leukocyte adhesion in inflammation
**作者**:Wang L, et al. (2020)
**摘要**:开发高特异性FUT4单克隆抗体,证明其能有效抑制中性粒细胞表面Sialyl Lewis X合成,减少炎症模型中白细胞与内皮细胞的黏附,为抗炎治疗提供新策略。
(注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献请通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词"FUT4 antibody"或"FUT8 knockout"等)
FUT4 antibody targets the human α-1.3-fucosyltransferase 4 (FUT4), also known as ELAM-1 ligand fucosyltransferase (ELC-1), a key enzyme in glycoconjugate biosynthesis. FUT4 catalyzes the transfer of fucose to terminal glycan structures, forming Lewis-type antigens like Lewis X (LeX) and sialyl-Lewis X (sLeX). These glycans play critical roles in cell-cell recognition, immune responses, and inflammatory processes. Notably, sLeX serves as a ligand for selectins, mediating leukocyte homing and cancer cell adhesion during metastasis. FUT4 is highly expressed in certain epithelial cancers, stem cells, and hematopoietic cells, correlating with tumor progression, drug resistance, and poor prognosis.
FUT4 antibodies are widely used in research to investigate glycosylation patterns in cancer biology, inflammation, and developmental processes. They enable detection of FUT4 expression via techniques like immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blotting. Such studies help clarify FUT4's regulatory mechanisms in pathological conditions and its potential as a therapeutic target. Commercially available FUT4 antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, validated for specificity against recombinant or native FUT4 protein. Their applications extend to biomarker discovery and evaluating glycosylation-targeted therapies in preclinical models.
×