
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
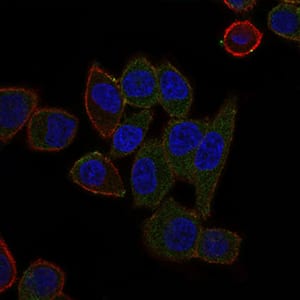
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
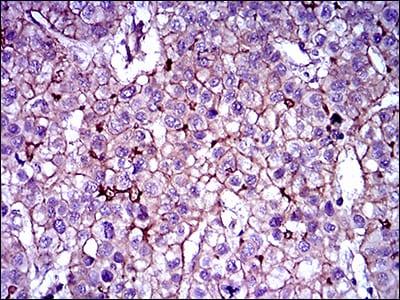
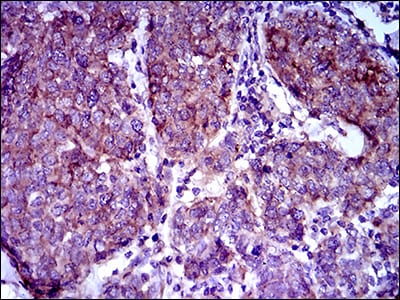
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
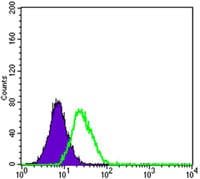
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
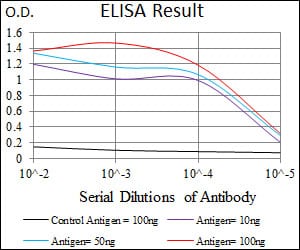
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ABCB5beta; EST422562; ABCB5alpha |
| Entrez GeneID | 340273 |
| clone | 5H3C6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 89.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ABCB5 (AA: 481-674) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于ABCB5抗体的3篇代表性文献,包含名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*ABCB5 identifies tumor-initiating cells in human melanoma*
**作者**:Schatton T, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用ABCB5特异性抗体,发现ABCB5在黑色素瘤干细胞表面高表达,并证明其通过调控干细胞自我更新和肿瘤生长促进癌症进展。ABCB5抗体阻断实验显著抑制了小鼠模型中肿瘤的形成能力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting ABCB5 antibody-mediated drug efflux in chemoresistant colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Frank NY, et al.
**摘要**:文章报道ABCB5在结直肠癌细胞中通过外排化疗药物(如5-FU)介导耐药性。使用ABCB5中和抗体可逆转耐药性,增强化疗敏感性,提示其作为克服肿瘤耐药性的潜在治疗靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**:*ABCB5 antibody-functionalized nanoparticles for targeted therapy in limbal stem cell deficiency*
**作者**:Kurze AK, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了ABCB5抗体偶联的纳米颗粒,用于靶向角膜缘干细胞(LSCs)。实验证明该抗体能特异性识别并富集ABCB5阳性的LSCs,促进角膜损伤修复,为眼科再生医学提供新策略。
---
这些文献分别从肿瘤干细胞标记、耐药机制干预及再生医学应用角度,揭示了ABCB5抗体的研究价值。如需具体文章链接或补充年份/期刊信息,可进一步说明。
ABCB5. a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family, is a transmembrane protein initially identified for its role in chemoresistance by effluxing therapeutic agents. It is expressed in normal tissues like skin, ocular epithelium, and gastrointestinal tract, where it regulates cell differentiation and stem cell maintenance. However, ABCB5 gained prominence as a biomarker for tumor-initiating cells (TICs) in cancers, particularly melanoma. Studies show ABCB5+ cancer cells drive tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance due to enhanced drug extrusion and stem-like properties.
ABCB5-specific antibodies, developed to target extracellular epitopes, have become critical tools for research and diagnostics. These monoclonal antibodies enable precise detection of ABCB5 expression via flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence, aiding in cancer cell isolation and characterization. Clinically, ABCB5 expression correlates with poor prognosis in melanoma, colorectal cancer, and glioblastoma, making it a potential biomarker for patient stratification.
Therapeutically, anti-ABCB5 antibodies are explored to inhibit ABCB5-mediated chemoresistance or directly target cancer stem cells. Preclinical models demonstrate that blocking ABCB5 enhances chemotherapy efficacy. Additionally, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or bispecific antibodies leveraging ABCB5’s surface expression are under investigation. Notably, ABCB5’s immunomodulatory role in regulatory T cells (Tregs) suggests potential synergy with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Early-phase trials for ABCB5-targeted therapies, particularly in refractory melanoma, highlight its translational relevance. Overall, ABCB5 antibodies bridge mechanistic insights into cancer stemness with emerging diagnostic and therapeutic applications. (298 words)
×