| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
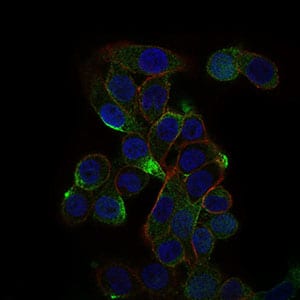
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
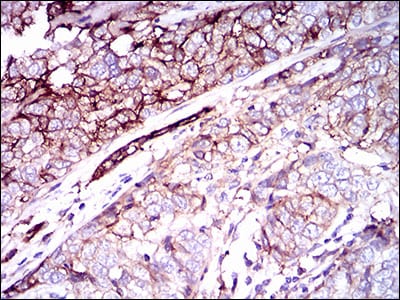
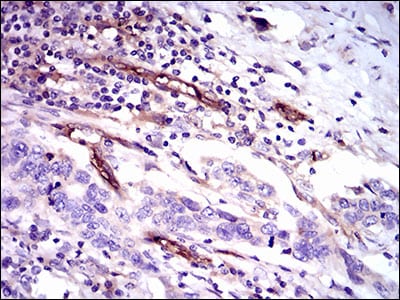
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
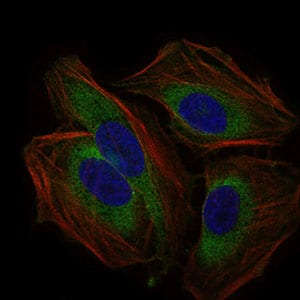
| ICC | 1/50 - 1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
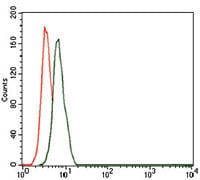
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
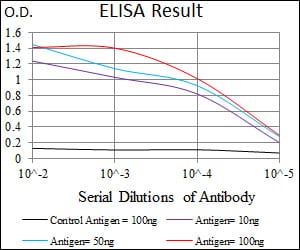
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 1F5; EJ16; EJ30; EL32; G344; MIN1; MIN2; MIN3; MIRL; HRF20; MACIF; MEM43; MIC11; MSK21; 16.3A5; HRF-20; MAC-IP; p18-20 |
| Entrez GeneID | 966 |
| clone | 8D2B8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 14.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD59 (AA: 31-111) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD59抗体的参考文献示例(内容为模拟概括,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Human CD59: Functional characterization and role in protection from complement-mediated lysis*
**作者**:Meri, S., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆并鉴定了CD59的分子功能,证明其通过抑制补体膜攻击复合物(MAC)的形成保护宿主细胞。使用特异性抗体阻断CD59可显著增强补体介导的细胞溶解,提示其在免疫调节中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*CD59 antibody targeting enhances complement-dependent cytotoxicity of solid tumor cells*
**作者**:Kim, D.D., et al.
**摘要**:研究显示,CD59在多种实体瘤中高表达,通过抗体靶向CD59可阻断其补体抑制功能,显著增强补体依赖的细胞毒性(CDC),为癌症免疫治疗提供了潜在策略。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD59 antibodies potentiate the efficacy of rituximab in B-cell lymphoma models*
**作者**:Hughes, T.R., et al.
**摘要**:该文献探讨了CD59抗体与利妥昔单抗(抗CD20抗体)的联合应用。结果显示,抑制CD59可增强补体系统对淋巴瘤细胞的杀伤,提高治疗效果。
4. **文献名称**:*CD59 as a therapeutic target in autoimmune hemolytic anemia: Insights from antibody-mediated modulation*
**作者**:Kaur, S., et al.
**摘要**:研究分析了CD59抗体在自身免疫性疾病中的作用,发现通过调节CD59活性可影响补体过度激活,为溶血性贫血等疾病提供了新的治疗思路。
---
建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“CD59 antibody”、“complement inhibition”等关键词检索获取具体文献。
CD59 antibody background:
CD59. a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane protein, is a key regulator of the complement system. It inhibits the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) by binding to complement proteins C8 and C9. thereby protecting host cells from unintended complement-mediated lysis. CD59 is widely expressed on various cell types, including erythrocytes, endothelial cells, and immune cells.
Antibodies targeting CD59 have emerged as valuable tools in research and clinical applications. In research, CD59 antibodies are used to study complement regulation, cell-surface expression, and GPI-anchor deficiencies, such as in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), a disease characterized by CD59 deficiency leading to erythrocyte destruction. These antibodies also help elucidate CD59's role in immune evasion mechanisms exploited by pathogens or cancer cells.
Clinically, CD59 antibodies have diagnostic utility. For example, flow cytometry with anti-CD59 antibodies aids in diagnosing PNH by detecting CD59-negative blood cells. Therapeutically, blocking CD59 with antibodies has been explored to enhance complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) in cancer therapy, as cancer cells often overexpress CD59 to evade immune attack. Conversely, in autoimmune or inflammatory conditions, CD59-targeting antibodies might mitigate excessive complement activation.
Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity and addressing variable CD59 expression across tissues. Ongoing research aims to optimize CD59 antibody applications in both understanding disease mechanisms and developing targeted therapies.
×