
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
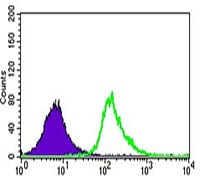
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Entrez GeneID | 8433 |
| clone | 5B6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human UTF1 (AA: 148-214) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于UTF1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**: "UTF1 maintains pluripotency by regulating chromatin accessibility in embryonic stem cells"
**作者**: Kristensen DM et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用UTF1抗体进行ChIP-seq分析,发现UTF1通过调控染色质开放状态维持胚胎干细胞多能性,与PRC2复合体协同抑制分化基因。
2. **文献名称**: "UTF1 as a novel biomarker for germ cell tumors: immunohistochemical validation"
**作者**: Nettersheim D et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化验证UTF1抗体在生殖细胞肿瘤中的特异性表达,证明其可作为精原细胞瘤和胚胎癌的可靠诊断标志物。
3. **文献名称**: "Dynamic expression of UTF1 during somatic cell reprogramming revealed by monoclonal antibody analysis"
**作者**: Okashita N, Kiso M et al.
**摘要**: 开发新型抗UTF1单克隆抗体,揭示其在体细胞重编程早期阶段动态表达模式,提示其在诱导多能性中的调控功能。
注:实际文献需通过PubMed/Web of Science等平台检索,建议使用关键词"UTF1 antibody"+"application"或结合具体研究领域筛选。
The UTF1 (Undifferentiated Embryonic Cell Transcription Factor 1) antibody is a tool used to study the UTF1 protein, a transcription regulator highly expressed in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and germ cells. UTF1 belongs to the PUFF (PGC/ESC-specific UTF-1 Associated Factor) family and plays a role in chromatin remodeling, transcriptional regulation, and maintaining pluripotency. It interacts with key pluripotency factors like Oct4. Sox2. and Nanog, and is implicated in modulating gene silencing and chromatin dynamics during early development. UTF1 expression decreases upon differentiation, suggesting its role in preserving the undifferentiated state of stem cells.
The UTF1 antibody is widely used in techniques such as chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), immunofluorescence (IF), and Western blotting (WB) to investigate pluripotency mechanisms, epigenetic regulation, and cellular reprogramming. It helps identify UTF1 binding sites on DNA, revealing its involvement in repressing developmental genes in ESCs. Studies also link UTF1 to Polycomb repressive complexes, highlighting its role in histone modification (e.g., H2AK119ub1) and gene silencing.
Additionally, UTF1 antibodies are utilized in cancer research, as UTF1 is abnormally expressed in certain tumors, potentially influencing oncogenesis. Researchers rely on its specificity for human, mouse, or other species to explore UTF1's dual role in stem cell biology and disease contexts. Its application advances understanding of early development, epigenetic landscapes, and regenerative medicine strategies.
×