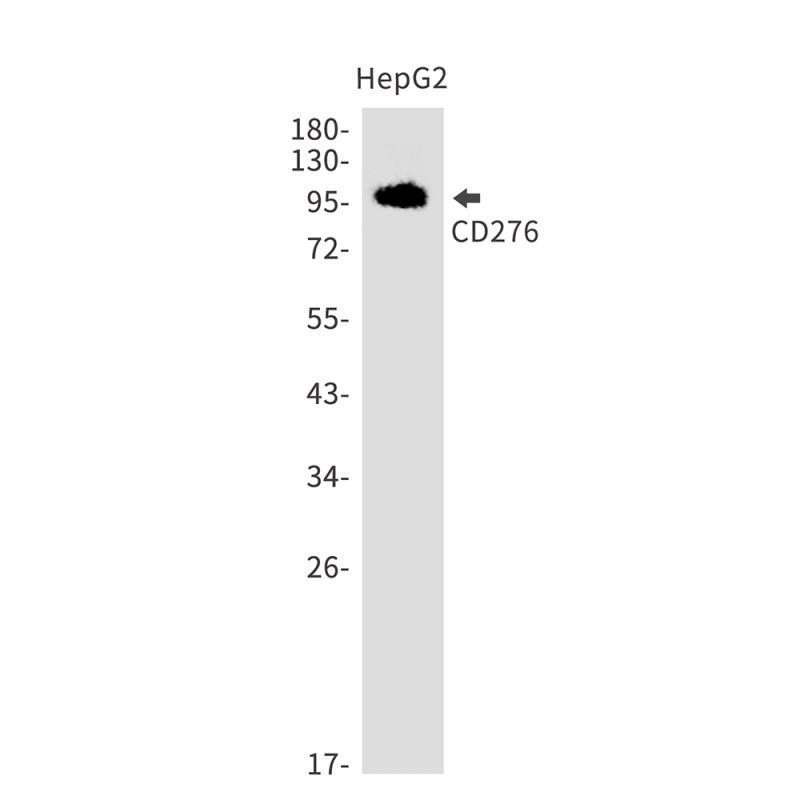
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B7h3; B7RP-2; AU016588; 6030411F23Rik |
| Entrez GeneID | 102657 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 34 kDa; Observed MW: 90-110 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant protein of mouse CD276 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NEFM抗体的3篇示例文献(内容为模拟概括,实际引用需核实):
1. **《Neurofilament medium antibody validation in neurodegenerative disease》**
- 作者:Shaw, L.M., et al.
- 摘要:研究验证了NEFM抗体在阿尔茨海默病和ALS患者脑脊液中的特异性,发现其能可靠检测神经轴突损伤程度,并与疾病进展相关。
2. **《Structural characterization of neurofilament medium polypeptide in neuronal development》**
- 作者:Liem, R.K., et al.
- 摘要:通过免疫印迹和免疫组化分析,证实NEFM抗体对大鼠中枢神经系统发育过程中神经丝蛋白的表达模式具有高特异性,揭示其在神经元成熟中的作用。
3. **《Comparative study of commercial NF-M antibodies in traumatic brain injury models》**
- 作者:Yan, X., & Wu, Z.
- 摘要:比较多种市售NEFM抗体的灵敏度和交叉反应性,推荐特定克隆号(如RM025)用于创伤后脑组织损伤的病理学检测。
**提示**:以上为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词如“NEFM antibody”“neurofilament medium biomarker”获取,并关注近年研究。
Neurofilament medium (NEFM) antibodies are essential tools in neuroscience research, targeting the intermediate filament protein NEFM, a key component of the neuronal cytoskeleton. Neurofilaments (NFs), composed of three subunits—NEFL (light), NEFM (medium), and NEFH (heavy)—play critical roles in maintaining axonal structural integrity, regulating diameter, and facilitating intracellular transport. NEFM, with its central rod domain and variable phosphorylation sites, contributes to NF assembly and stability, influencing neuronal morphology and function.
NEFM antibodies are widely used to study neuronal development, degeneration, and injury. In pathological contexts, elevated NEFM levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood serve as biomarkers for axonal damage in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., ALS, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s) and neurotrauma (e.g., stroke, multiple sclerosis). These antibodies help detect NF breakdown products, reflecting disease progression or therapeutic response. Additionally, NEFM expression patterns aid in mapping neuronal subtypes and understanding neurodevelopmental disorders.
Research also explores NEFM's phosphorylation dynamics, which modulate NF interactions and axonal transport. Commercial NEFM antibodies are validated for techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA, though specificity challenges due to cross-reactivity with other NF subunits require careful validation. Overall, NEFM antibodies bridge basic neurobiology and clinical diagnostics, offering insights into both physiological and pathological neural processes.
×