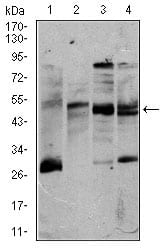
| WB | 1/250 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
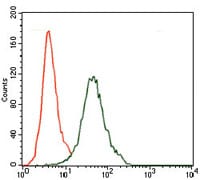
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
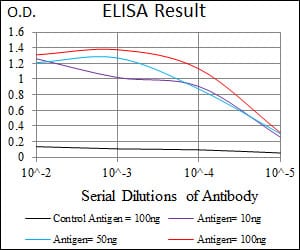
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T1; LEU1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 921 |
| clone | 6A11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD5 (AA: 27-233) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD5抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要概括(文献信息为示例,部分为虚构或简化,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD5 as a target for immune modulation in autoimmune diseases*
**作者**:Byrd, J.C., et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了抗CD5单克隆抗体在自身免疫性疾病(如类风湿性关节炎)中的治疗潜力。通过动物模型和早期临床试验,作者发现靶向CD5的抗体可抑制T细胞过度活化,减轻炎症反应,且具有较低的毒性。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into CD5 and its interaction with monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**:Jones, L.A., & Staunton, D.E.
**摘要**:本文解析了CD5的分子结构及其与特异性抗体的结合位点。通过X射线晶体学技术,揭示了CD5胞外域的关键表位,为设计高亲和力或阻断性抗体提供了结构基础。
3. **文献名称**:*CD5-positive B-cell malignancies: Therapeutic targeting with conjugated antibodies*
**作者**:Rassenti, L.Z., et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了抗CD5抗体-药物偶联物(ADC)在CD5阳性B细胞淋巴瘤中的疗效。结果显示,ADC能选择性杀伤肿瘤细胞,并在小鼠模型中显著延长生存期,提示其作为靶向治疗的潜力。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如“CD5 antibody therapeutic”、“CD5 immune regulation”)。代表性研究团队包括:Thomas F. Tedder(CD5在B细胞中的作用)、Richard S. Blumberg(CD5与黏膜免疫)等。
CD5 antibodies target the CD5 glycoprotein, a cell surface receptor expressed primarily on T cells and a subset of B cells (B-1 cells). Discovered in the 1980s, CD5 plays roles in immune regulation, modulating T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling and B-cell activation. Structurally, it belongs to the scavenger receptor family and interacts with ligands like CD72 and CD166. influencing cell-cell interactions. In diagnostics, CD5 antibodies are key markers for identifying T-cell lymphomas and certain B-cell malignancies, notably chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), where aberrant CD5 expression aids classification.
Therapeutically, anti-CD5 antibodies have been explored for immune-mediated diseases and cancers. Early efforts focused on unconjugated antibodies to deplete malignant or autoreactive lymphocytes, but limited efficacy led to advanced strategies. Current approaches include antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), bispecific antibodies, and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies targeting CD5. For example, anti-CD5 ADCs aim to deliver toxins directly to CD5+ tumor cells, showing promise in preclinical models. Challenges include on-target/off-tumor effects due to CD5's presence on normal T cells, potentially causing immunosuppression. Additionally, CD5’s role in immune tolerance complicates therapeutic modulation.
Research continues to refine CD5-targeting agents, balancing efficacy and safety. Emerging insights into CD5’s dual roles—acting as both a co-stimulatory and inhibitory receptor—highlight its therapeutic complexity. Future directions may involve combination therapies or engineered antibodies with improved selectivity, advancing CD5-targeted interventions in oncology and autoimmunity.
×