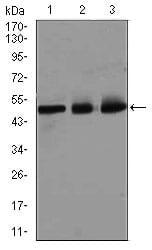
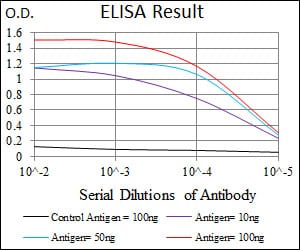
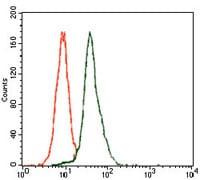
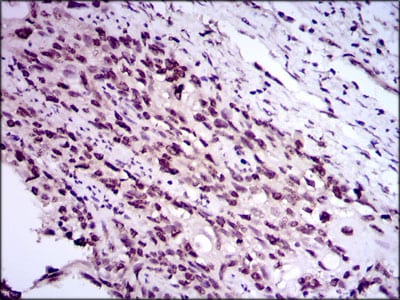
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
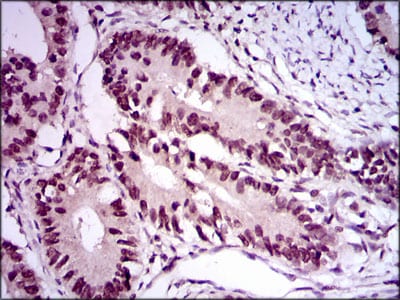
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RBP3; E2F-1; RBAP1; RBBP3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1869 |
| clone | 8G9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human E2F1 (AA: 69-223) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
The E2F1 antibody is a crucial tool in molecular biology for studying the E2F1 transcription factor, a key regulator of cell cycle progression and apoptosis. E2F1 belongs to the E2F family of proteins, which control the transition from the G1 to S phase by regulating genes essential for DNA replication and cell division. E2F1 activity is tightly controlled through interactions with the retinoblastoma (Rb) protein; Rb binding inhibits E2F1 until phosphorylation of Rb during late G1 phase releases E2F1. enabling transcriptional activation of target genes such as cyclin E and CDK2. Beyond its role in cell cycle regulation, E2F1 is implicated in DNA damage responses, differentiation, and oncogenesis, acting as both an oncogene and tumor suppressor depending on cellular context. Dysregulation of E2F1 is linked to cancers, making it a focus of therapeutic research.
E2F1 antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to detect E2F1 expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. They help elucidate E2F1’s role in disease mechanisms, drug responses, and cellular pathways. Validated antibodies ensure specificity, often confirmed via knockout cell lines or siRNA knockdown. Researchers rely on these antibodies to explore E2F1’s dual functions in proliferation and apoptosis, offering insights into cancer biology and potential treatment strategies.
×