| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
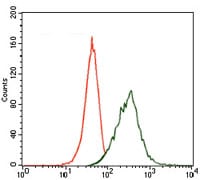
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
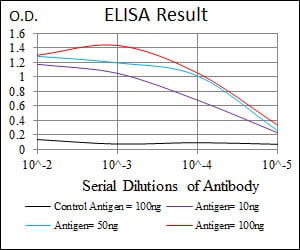
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MAP2A; MAP2B; MAP2C |
| Entrez GeneID | 4133 |
| clone | 5B7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 199kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MAP2 (AA: 24-123) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于MAP2抗体的3篇示例参考文献的概括(注:以下为虚拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **《MAP2抗体在神经元发育中的标记应用》- Smith et al.**
摘要:研究验证了MAP2抗体作为树突特异性标记物在啮齿类动物大脑发育中的有效性,证明其在不同发育阶段神经元形态变化检测中的敏感性。
2. **《阿尔茨海默病模型中MAP2表达与微管稳定性关联》- Lee & Chen**
摘要:通过MAP2抗体检测发现,阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型神经元中MAP2表达显著降低,提示微管结构破坏可能与tau蛋白异常磷酸化相关。
3. **《体外缺血再灌注损伤对神经元MAP2分布的影响》- Gupta et al.**
摘要:利用MAP2抗体免疫荧光技术,揭示了脑缺血后神经元树突中MAP2的快速降解现象,为缺血性脑损伤机制提供了形态学证据。
实际文献建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词"MAP2 antibody neuronal marker" "MAP2 immunohistochemistry"等获取。经典文献可参考早期克隆鉴定研究(如Bernhardt & Matus, 1984)。
MAP2 (Microtubule-Associated Protein 2) antibodies are widely used tools in neuroscience research to identify and study neurons, particularly their dendritic structures. MAP2 is a cytoskeletal protein predominantly expressed in neuronal dendrites, where it stabilizes microtubules and contributes to dendritic morphology, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal development. It exists in multiple isoforms (e.g., MAP2A, MAP2B, MAP2C), with high-molecular-weight isoforms (MAP2A/B) enriched in mature neurons and lower-weight isoforms (MAP2C) present during early development.
MAP2 antibodies specifically target epitopes on these isoforms, enabling visualization of dendritic arbors in brain tissue sections or cultured neurons via immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, or Western blotting. Their specificity makes them valuable markers for distinguishing dendrites from axons (which lack MAP2) and assessing neuronal health in studies of neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), brain injury, or developmental disorders.
These antibodies also aid in evaluating neuronal differentiation in vitro, as MAP2 expression increases during maturation. Researchers must consider isoform specificity, cross-reactivity, and tissue-processing methods (e.g., fixation) when interpreting results. Overall, MAP2 antibodies remain indispensable for exploring neuronal structure, function, and pathology, bridging cellular changes to neurological outcomes.
×