| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
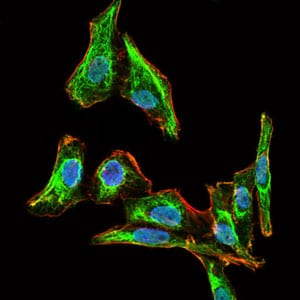
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
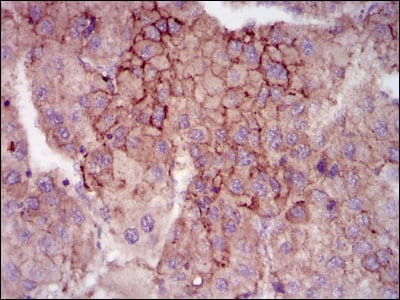
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
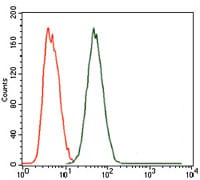
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
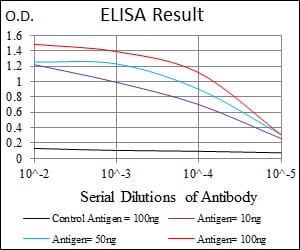
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HPK38 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9833 |
| clone | 2G2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of human MELK(AA: 637-651:C-VYKRLVEDILSSCKV). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于MELK(母胚亮氨酸拉链激酶)抗体的代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*MELK is an oncogenic kinase essential for mitotic progression in basal-like breast cancer cells*
**作者**:Jiang P. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过特异性MELK抗体验证了MELK在基底样乳腺癌细胞中的高表达,并发现抑制MELK活性可显著降低肿瘤细胞的增殖和体内成瘤能力,表明其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a novel monoclonal antibody for MELK-specific detection in human cancers*
**作者**:Park Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高特异性的抗MELK单克隆抗体,验证了其在多种癌症组织(如胶质母细胞瘤、结肠癌)中的免疫组化应用,并证明MELK表达与患者预后不良相关。
3. **文献名称**:*MELK as a potential therapeutic target in cancer stem cells: Role of antibody-based targeting*
**作者**:Lin A. et al.
**摘要**:文章探讨了MELK在癌症干细胞中的关键作用,利用MELK抗体阻断其功能后显著抑制了肿瘤自我更新能力,提示其可作为联合治疗策略的靶点。
4. **文献名称**:*Functional characterization of MELK in DNA damage repair through antibody-mediated depletion*
**作者**:Gu C. et al.
**摘要**:通过MELK抗体敲低实验,揭示了MELK通过调控ATR/Chk1信号通路参与DNA损伤修复,为MELK抑制剂在放化疗增敏中的应用提供理论支持。
---
以上文献覆盖了MELK抗体的功能验证、治疗潜力及机制研究,适用于靶向治疗开发或生物标志物探索。如需具体年份或期刊信息,可进一步补充检索条件。
The Maternal Embryonic Leucine zipper Kinase (MELK) is a serine/threonine kinase belonging to the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) family. Initially identified for its role in embryonic development and stem cell regulation, MELK is overexpressed in numerous cancers, including breast, glioblastoma, and prostate cancer, where it correlates with poor prognosis. It participates in cell cycle progression, apoptosis resistance, DNA damage repair, and maintenance of cancer stem cells. MELK’s oncogenic functions are attributed to its interactions with key signaling pathways, such as TGF-β, Wnt, and Hippo, making it a potential therapeutic target.
MELK antibodies are essential tools for detecting MELK expression in research and diagnostics. They enable quantification of MELK levels in tissues or cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Recent studies, however, highlight controversies: while some evidence supports MELK’s critical role in tumor survival, genetic knockout models occasionally show no phenotypic changes, suggesting context-dependent functions or compensatory mechanisms. Despite this, MELK remains a focus in cancer biology, with inhibitors undergoing preclinical evaluation. Reliable MELK antibodies are crucial for elucidating its complex roles and advancing targeted therapies.
×