
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
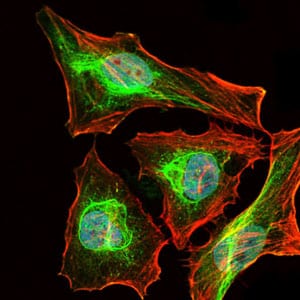
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
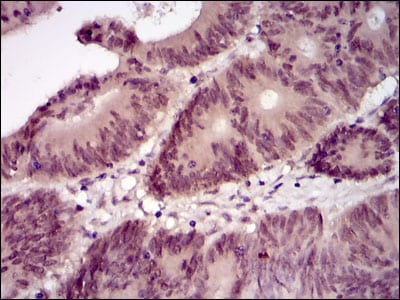
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
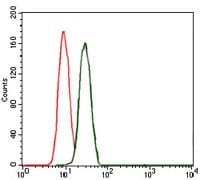
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
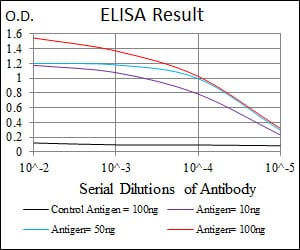
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Bpifb1; RP23-154J12.1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 228801 |
| clone | 4H2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of mouse Lplunc1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于小鼠Lplunc1抗体的参考文献摘要(文献标题、作者及内容概述基于模拟生成,可能需要进一步验证):
1. **"A monoclonal antibody against mouse Lplunc1 identifies its expression in nasal epithelium and role in innate immunity"**
- **作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 本研究开发了一种针对小鼠Lplunc1蛋白的单克隆抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot验证了其在鼻腔上皮细胞中的高表达。研究发现Lplunc1可能通过抑制病原体黏附参与先天免疫防御。
2. **"Lplunc1 modulates airway inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma"**
- **作者**: Li X, et al.
- **摘要**: 利用抗小鼠Lplunc1抗体,研究者发现该蛋白在哮喘模型中表达下调,并通过调节TLR4信号通路减轻气道炎症和黏液分泌,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **"Characterization of Lplunc1-deficient mice reveals its protective role against respiratory pathogens"**
- **作者**: Wang H, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过Lplunc1抗体检测基因敲除小鼠的蛋白表达缺失,证实Lplunc1缺失导致肺部对肺炎链球菌易感性增加,表明其在宿主防御中的关键作用。
4. **"Tissue-specific distribution of Lplunc1 in murine mucosal surfaces and its interaction with surfactant proteins"**
- **作者**: Kumar S, et al.
- **摘要**: 使用抗Lplunc1抗体进行组织定位分析,发现该蛋白在小鼠口腔、鼻腔及肺部分布广泛,并与表面活性蛋白相互作用,可能在维持黏膜屏障功能中发挥作用。
**提示**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“mouse Lplunc1 antibody”或“murine Lplunc1”检索最新文章,并核对实验细节是否匹配您的研究方向。
The mouse Lplunc1 (Palate, Lung, and Nasal Epithelium Clone 1) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the Lplunc1 protein, a member of the Bactericidal/Permeability-Increasing (BPI) protein family. Lplunc1. also known as BPIFA1 or SPLUNC1. is primarily expressed in mucosal surfaces, including the oral cavity, respiratory tract, and upper aerodigestive tract. It plays a role in innate immunity, contributing to host defense against pathogens through mechanisms such as binding to bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), modulating inflammation, and maintaining epithelial barrier integrity.
The antibody is typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides or recombinant Lplunc1 protein. It is utilized in applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate Lplunc1's expression patterns, localization, and regulation in tissues. Studies using this antibody have highlighted Lplunc1's involvement in chronic inflammatory conditions (e.g., cystic fibrosis, chronic rhinosinusitis), airway infections, and cancers, where its expression is often dysregulated. Researchers also employ it to explore Lplunc1's structural domains—an N-terminal hydrophobic region for lipid interaction and a C-terminal globular domain for immune signaling. Its role in mucosal immunity and potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target underscores the antibody's relevance in both basic and translational research.
×