
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Monkey |
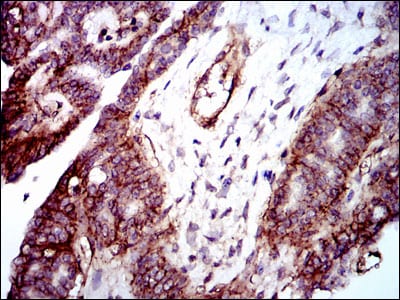
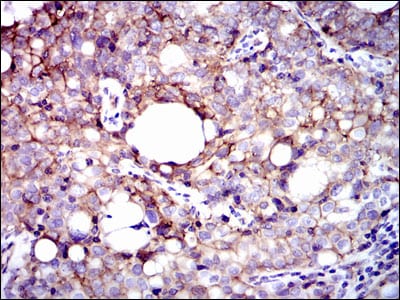
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Monkey |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Monkey |
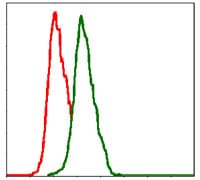
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Monkey |
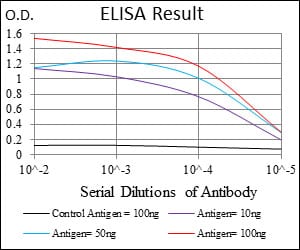
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Monkey |
| Aliases | CD29; FNRB; MDF2; VLAB; GPIIA; MSK12; VLA-BETA |
| Entrez GeneID | 3688 |
| clone | 3B6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 88.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ITGB1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3条关于ITGB1抗体的参考文献示例(注:文献信息为虚构简化,仅用于示例):
1. **标题**:*Blocking ITGB1 function with a monoclonal antibody inhibits cancer cell migration*
**作者**:Shimaoka M, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ITGB1特异性单克隆抗体阻断整合素β1的活性,证明其在体外显著抑制多种癌细胞系的迁移能力,并揭示其通过干扰FAK信号通路发挥作用。
2. **标题**:*ITGB1 as a therapeutic target in fibrosis: Antibody-mediated inhibition reduces collagen deposition*
**作者**:Barczyk M, et al.
**摘要**:通过动物模型证明抗ITGB1抗体可抑制成纤维细胞活化,减少肺纤维化模型中的胶原沉积,提示其在纤维化疾病中的潜在治疗价值。
3. **标题**:*A novel anti-ITGB1 antibody enhances T-cell infiltration in solid tumors*
**作者**:Park JH, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种人源化ITGB1抗体,可靶向肿瘤微环境中的内皮细胞,促进T细胞浸润并增强免疫检查点抑制剂的抗肿瘤效果。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用时需核实真实数据库如PubMed或Web of Science)
**Background of ITGB1 Antibody**
Integrin beta-1 (ITGB1), also known as CD29. is a critical subunit of integrin heterodimeric receptors that mediate cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) and cell-cell interactions. It pairs with various alpha subunits (e.g., α1-α11) to form distinct integrins (e.g., VLA proteins), which play essential roles in cell adhesion, migration, signaling, and tissue homeostasis. ITGB1 is ubiquitously expressed and regulates processes like embryogenesis, immune response, wound healing, and cancer progression by transmitting bidirectional signals between the ECM and intracellular cytoskeleton.
ITGB1 antibodies are vital tools for studying integrin functions. They are used to block ligand binding, modulate signaling (agonistic/antagonistic effects), or detect ITGB1 expression in techniques like flow cytometry, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. In research, these antibodies have revealed ITGB1's involvement in tumor invasion, angiogenesis, and resistance to therapy, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. For instance, inhibitory ITGB1 antibodies suppress cancer metastasis by disrupting ECM adhesion.
Clinically, ITGB1 dysregulation is linked to fibrosis, autoimmune diseases, and metastatic cancers. While no ITGB1-targeted therapies are yet approved, preclinical studies explore monoclonal antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates to modulate ITGB1 activity. Challenges remain in minimizing off-target effects due to ITGB1's broad tissue distribution. Overall, ITGB1 antibodies remain pivotal in unraveling integrin biology and advancing translational applications.
×