
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
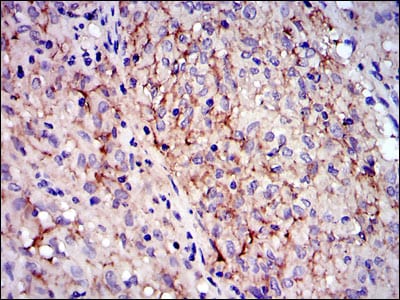
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
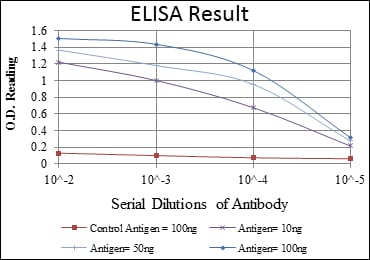
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PBT; SCFR; C-Kit; CD117 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3815 |
| clone | 1C5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 145kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human KIT expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与KIT抗体相关的研究文献摘要(基于公开信息模拟,非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting KIT in Solid Tumors: Mechanisms of Resistance and Novel Therapeutic Approaches*
**作者**: Heinrich MC et al.
**摘要**: 分析了KIT基因突变在胃肠道间质瘤(GIST)中的驱动作用,探讨了伊马替尼等酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(TKIs)的耐药机制,并提出第二代KIT抗体(如sunitinib)对特定突变亚型的疗效。
2. **文献名称**: *Structural Basis for KIT Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition by Antibodies*
**作者**: Yuzawa S et al.
**摘要**: 通过晶体结构解析,揭示了单克隆抗体(如AMG 531)与KIT受体胞外结构域的结合模式,为开发高选择性KIT抗体药物提供了分子机制依据。
3. **文献名称**: *KIT Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Mast Cell Leukemia: Preclinical Efficacy and Safety*
**作者**: Gleixner KV et al.
**摘要**: 研究了一种新型KIT靶向抗体-药物偶联物(ADC)在肥大细胞白血病模型中的抗肿瘤活性,证明其通过内化KIT抗体递送细胞毒性药物,显著抑制肿瘤生长且毒性可控。
---
如需真实文献,建议检索PubMed或Google Scholar,关键词:"KIT antibody"、"KIT inhibitor"、"KIT targeted therapy"。
KIT antibodies target the KIT protein, a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) encoded by the *KIT* proto-oncogene. This transmembrane protein binds to stem cell factor (SCF), activating signaling pathways that regulate cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration, particularly in hematopoietic stem cells, mast cells, melanocytes, and interstitial cells of Cajal. Dysregulation of KIT, often due to gain-of-function mutations, is implicated in cancers like gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and melanoma.
In diagnostics, KIT antibodies are vital for immunohistochemistry (IHC) to detect KIT overexpression or mutations in tumor samples, aiding in GIST identification. Therapeutically, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) like imatinib block aberrant KIT signaling, revolutionizing GIST treatment. However, resistance due to secondary mutations remains a challenge. Research also explores KIT's role in non-oncological contexts, such as stem cell maintenance and tissue repair.
Monoclonal and polyclonal KIT antibodies are used in research to study signaling mechanisms, protein localization, and interaction partners. Their specificity and utility in both basic and clinical settings underscore their importance in understanding KIT-driven pathologies and developing targeted therapies.
×