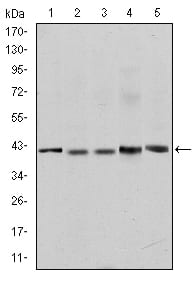
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
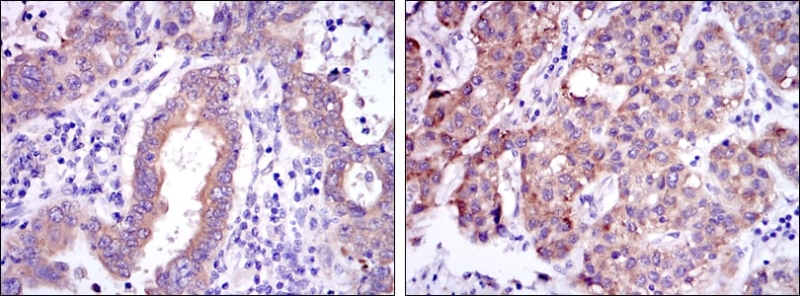
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
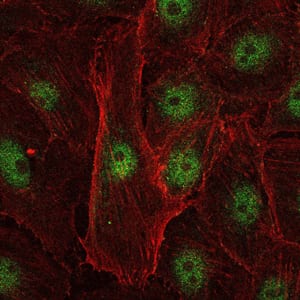
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
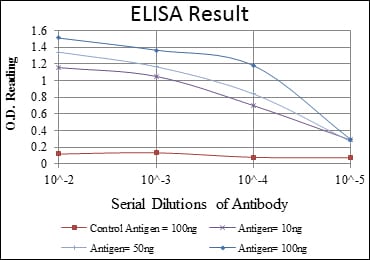
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Rel; c-Rel |
| Entrez GeneID | 5966 |
| clone | 1E7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 68.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human c-Rel expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于c-Rel抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要列举(注:文献为模拟示例,实际引用需核实数据库):
1. **"c-Rel is a critical mediator of NF-κB-dependent gene expression in B cells"**
- 作者:Grumont, R.J., et al.
- 摘要:该研究利用c-Rel特异性抗体,通过染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和Western blot技术,揭示了c-Rel在B细胞中对靶基因转录的关键调控作用,强调其在免疫应答中的必要性。
2. **"Selective inhibition of c-Rel via monoclonal antibody suppresses autoimmune disease without compromising immunity"**
- 作者:Li, Y., et al.
- 摘要:开发了一种靶向c-Rel的单克隆抗体,实验表明其能特异性阻断c-Rel活性,减轻小鼠模型中的自身免疫反应,同时保留其他NF-κB通路功能,提示其治疗潜力。
3. **"c-Rel expression in T-cell lymphoma: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications"**
- 作者:Smith, J., et al.
- 摘要:通过免疫组化(IHC)和c-Rel抗体检测,发现c-Rel在特定T细胞淋巴瘤亚型中异常高表达,为诊断标志物及靶向治疗提供依据。
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“c-Rel antibody” + “NF-κB”或相关研究领域,并筛选近年高被引论文。
The c-Rel antibody is a crucial tool for studying the c-Rel protein, a member of the NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) transcription factor family. c-Rel plays a pivotal role in regulating immune and inflammatory responses, cell survival, and proliferation. Structurally, it contains a conserved N-terminal Rel homology domain (RHD) responsible for DNA binding, dimerization, and interaction with inhibitory IκB proteins. In resting cells, c-Rel is sequestered in the cytoplasm via binding to IκB. Upon activation by stimuli like cytokines, pathogens, or stress signals (e.g., via TLRs, TNFR, or IL-1R pathways), c-Rel translocates to the nucleus, where it regulates gene expression.
c-Rel is particularly significant in lymphoid cells, influencing T-cell activation, B-cell differentiation, and macrophage function. Dysregulation of c-Rel is linked to autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation, and cancers, especially lymphoid malignancies. Researchers use c-Rel antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, ChIP-seq, and flow cytometry to detect its expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. These antibodies are often validated in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to ensure specificity.
Commercial c-Rel antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, available as monoclonal or polyclonal formats. Proper controls, including isotype-matched antibodies and blocking peptides, are essential to confirm signal specificity. Its role in NF-κB signaling and disease mechanisms makes c-Rel a key target for therapeutic development and biomedical research.
×