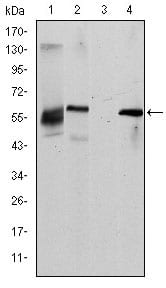
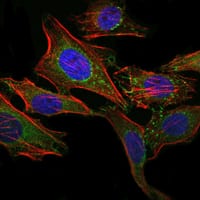
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
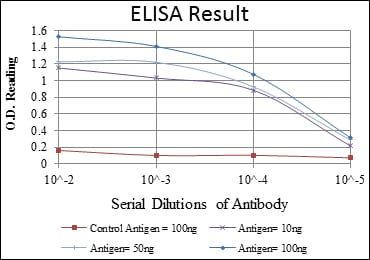
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Aliases | MRX; MXR; ABCP; BCRP; BMDP; MXR1; ABC15; BCRP1; CD338; CDw338; EST157481; MGC102821 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9429 |
| clone | 1H2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 72kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ABCG2 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ABCG2抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*ABCG2: A potential marker of cancer stem cells and therapeutic target*
**作者**:Nakanishi T, Ross DD
**摘要**:该综述探讨了ABCG2蛋白在癌症干细胞中的高表达及其介导的多药耐药性机制,强调了特异性抗体在检测ABCG2表达及靶向治疗研究中的应用价值。
2. **文献名称**:*Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for human ABCG2*
**作者**:Zhou S, Schuetz JD, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了针对人类ABCG2蛋白的单克隆抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证其特异性,证实该抗体可用于检测细胞膜ABCG2的表达水平及功能研究。
3. **文献名称**:*The role of ABCG2 in modulating responses to anti-cancer agents*
**作者**:Robey RW, Polgar O, et al.
**摘要**:本文利用ABCG2特异性抗体揭示了该转运蛋白在癌细胞中的过表达导致化疗药物外排增强,并提出抑制ABCG2可逆转耐药性,为联合用药策略提供依据。
4. **文献名称**:*ABCG2-overexpressing mammary stem cells contribute to tumor chemoresistance*
**作者**:Bunting KD, Zhou S, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组织化学分析,研究发现乳腺癌干细胞中ABCG2高表达与化疗药物外排相关,特异性抗体标记证实其在肿瘤微环境中的功能活性。
The ABCG2 antibody is a crucial tool for studying the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter subfamily G member 2. also known as breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). ABCG2 is a transmembrane protein involved in multidrug resistance (MDR), primarily by exporting a wide range of endogenous and exogenous substrates, including chemotherapeutic agents, toxins, and metabolic byproducts. It plays a vital role in physiological barriers such as the blood-brain, placental, and intestinal barriers, regulating absorption, distribution, and excretion of compounds. Overexpression of ABCG2 in cancer cells is linked to reduced drug efficacy, as it pumps chemotherapeutics out of cells, promoting tumor survival.
ABCG2 antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression and localization via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. They help elucidate ABCG2's role in drug resistance, tissue protection, and stem cell maintenance (e.g., side population stem cells marked by ABCG2 activity). Additionally, these antibodies aid in studying genetic variants and post-translational modifications affecting transporter function. In therapeutic contexts, ABCG2-targeting strategies, including inhibitory antibodies or small molecules, aim to overcome chemoresistance. Beyond cancer, ABCG2 is implicated in diseases like gout (urate excretion) and neurodegenerative disorders (amyloid-beta transport). Its dual role as a protector against toxins and a contributor to treatment failure underscores its biomedical significance, making ABCG2 antibodies essential for both mechanistic studies and translational applications.
×