
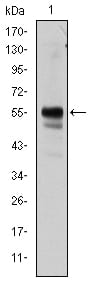
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AML1; CBFA2; EVI-1; AMLCR1; PEBP2aB; AML1-EVI-1; RUNX1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 861 |
| clone | 2B5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of human RUNX1. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于RUNX1抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **"RUNX1 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia"**
- Authors: Wang, Q., et al. (2014)
- 摘要:研究通过Western blot和免疫组化使用RUNX1抗体,发现其突变与白血病发生相关,强调了该抗体在肿瘤研究中的诊断价值。
2. **"AML1. the target of multiple chromosomal translocations in human leukemia, is essential for normal fetal liver hematopoiesis"**
- Authors: Okuda, T., et al. (1996)
- 摘要:首次报道了针对RUNX1(AML1)的多克隆抗体制备,验证其在造血发育中的关键作用,并用于检测基因敲除小鼠模型中的蛋白表达缺失。
3. **"The RUNX1 transcription factor: A multifunctional regulator of hematopoiesis"**
- Authors: Ito, Y., et al. (2015)
- 摘要:综述中讨论了多种RUNX1抗体的应用(如ChIP-seq、流式细胞术),解析其在造血分化、白血病中的调控网络,比较了不同抗体的特异性差异。
4. **"Cloning and characterization of subunits of the T-cell receptor and murine leukemia virus enhancer core-binding factor"**
- Authors: Miyoshi, H., et al. (1991)
- 摘要:早期研究克隆了RUNX1基因并开发了兔源多克隆抗体,通过免疫沉淀验证其与DNA结合功能,为后续机制研究奠定基础。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性内容,实际引用时请核对原文准确性。)
The RUNX1 antibody is a critical tool in studying the RUNX1 protein, a transcription factor encoded by the *RUNX1* gene (previously known as *AML1*). RUNX1 belongs to the RUNX family of transcription factors, which regulate gene expression by binding to DNA through a conserved Runt domain. It plays a pivotal role in hematopoiesis, particularly in the development of hematopoietic stem cells and differentiation of myeloid and lymphoid lineages. Dysregulation of RUNX1 is strongly associated with hematologic malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). For example, the t(8;21) translocation in AML generates the RUNX1-ETO fusion protein, disrupting normal hematopoietic regulation.
RUNX1 antibodies are widely used in research to detect RUNX1 expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). These antibodies are essential for investigating RUNX1’s role in normal and malignant cells, including its involvement in transcriptional networks, epigenetic modifications, and signaling pathways. Specific antibody clones are validated for applications in different experimental models, such as cell lines, primary tissues, or animal models.
The development and validation of RUNX1 antibodies require rigorous testing for specificity, sensitivity, and cross-reactivity, given the structural homology among RUNX family members. Reliable antibodies have advanced studies on RUNX1’s dual roles as an oncogene or tumor suppressor, depending on cellular context and mutational status. Their utility extends to clinical diagnostics, aiding in the classification of leukemias and monitoring residual disease. Overall, RUNX1 antibodies remain indispensable for both basic research and translational applications in hematology and oncology.
×