| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
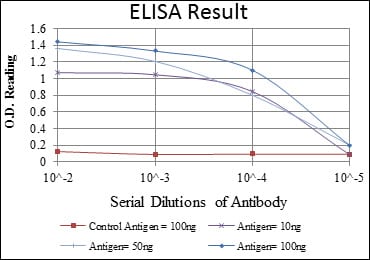
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CEA; CD66e; DKFZp781M2392; CEACAM5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1048 |
| clone | 3G12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 77kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CEA expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CEA抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: *"Development of a Humanized Anti-CEA Antibody for Immuno-PET Imaging of Colorectal Cancer"*
**作者**: Knowles SM 等
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种人源化抗CEA单克隆抗体(mAb),用于结直肠癌的免疫PET成像。该抗体在小鼠模型中显示出高特异性结合CEA的能力,并成功实现了肿瘤病灶的高对比度显像,为癌症早期诊断提供了新工具。
2. **文献名称**: *"Bispecific Antibodies Targeting CEA and CD3 Enhance T Cell-Mediated Killing of CEA-Positive Tumor Cells"*
**作者**: Zhukovsky EA 等
**摘要**: 本文设计了一种同时靶向CEA和T细胞表面CD3的双特异性抗体,通过激活T细胞并引导其攻击CEA阳性肿瘤细胞,显著提高了体外和动物模型中的抗肿瘤效果,为实体瘤免疫治疗提供了新策略。
3. **文献名称**: *"A Novel Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on CEA Antibody-Modified Gold Nanoparticles for Ultrasensitive Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen"*
**作者**: Wang Y 等
**摘要**: 研究提出了一种基于金纳米颗粒修饰的抗CEA抗体电化学传感器,利用纳米材料放大信号,实现了血清中CEA的超灵敏检测(检测限低至0.1 pg/mL),在癌症筛查和预后监测中潜力显著。
4. **文献名称**: *"CEA-Specific CAR-T Cells with Dual Targeting Antibodies Show Enhanced Efficacy in Solid Tumors"*
**作者**: Liu X 等
**摘要**: 该研究通过结合抗CEA抗体与嵌合抗原受体(CAR)T细胞技术,开发了双重靶向CEA的CAR-T细胞。实验表明,改造后的T细胞对高表达CEA的胰腺癌和结直肠癌细胞具有更强的杀伤活性,且减少了脱靶毒性。
以上文献涵盖诊断成像、免疫治疗、生物传感技术等方向,反映了CEA抗体在癌症研究中的多样化应用。
**Background of CEA Antibodies**
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), a glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, was first identified in 1965 as a tumor-associated antigen in colorectal cancer. It is overexpressed in many epithelial-derived cancers, including gastrointestinal, lung, and breast cancers, as well as in certain nonmalignant conditions (e.g., inflammation). CEA plays roles in cell adhesion, immune modulation, and metastasis, though its exact physiological functions remain under study.
CEA antibodies are immunoglobulins designed to specifically bind CEA, enabling its detection and quantification. In diagnostics, CEA antibodies are widely used in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, immunohistochemistry) to measure serum CEA levels, aiding cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of recurrence. Elevated CEA levels correlate with tumor burden and treatment response.
Therapeutically, anti-CEA monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been explored for targeted cancer therapy. Engineered mAbs, such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or radioimmunotherapy agents, aim to deliver cytotoxic payloads directly to CEA-expressing tumors, minimizing systemic toxicity. Additionally, CEA antibodies are utilized in imaging techniques (e.g., immuno-PET) to localize tumors and metastases.
Despite clinical utility, challenges include CEA's expression in normal tissues and non-specific elevation in benign conditions, affecting specificity. Ongoing research focuses on improving antibody affinity, developing bispecific antibodies, and combining CEA-targeting strategies with immunotherapies to enhance precision and efficacy in oncology.
×