| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
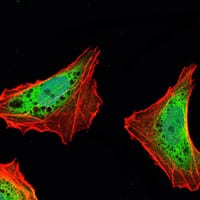
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
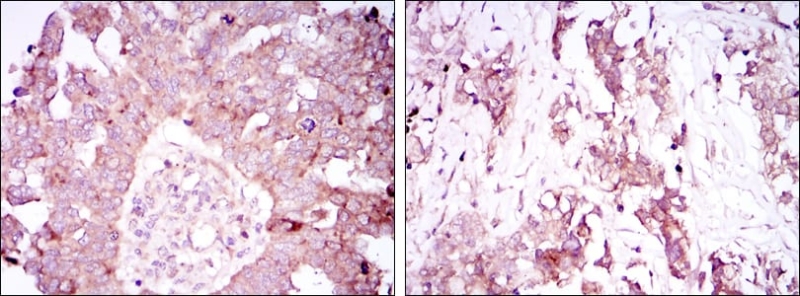
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
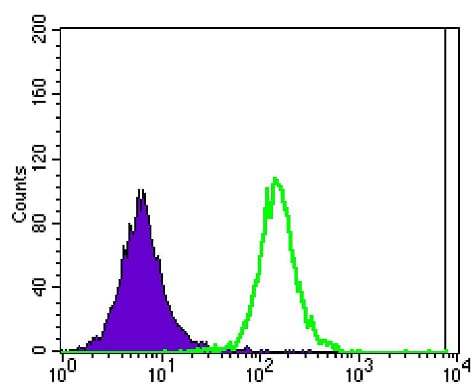
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ATX1; SCA1; D6S504E; ATXN1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6310 |
| clone | 2F5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 87kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ATXN1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及ATXN1抗体的研究文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxias: clinical features, genetics, and pathogenesis"*
**作者**: Orr, H.T., Chung, M.Y., Banfi, S., et al. (1993)
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆了SCA1致病基因,发现其编码ATXN1蛋白。研究利用ATXN1特异性抗体检测到突变蛋白在小脑浦肯野细胞中的异常聚集,揭示了ATXN1的核内定位与神经退行性变的关联。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Basis for the mechanims of phosphoregulation in ataxin-1 neurodegeneration"*
**作者**: Duvick, L., Barnes, J., Ebner, B.A., et al. (2010)
**摘要**: 通过ATXN1磷酸化特异性抗体,研究发现ATXN1的Ser776位点磷酸化调控其稳定性及与转录抑制复合物的结合,阐明了磷酸化修饰在SCA1病理中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Antisense oligonucleotide therapy for spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 ameliorates disease phenotypes in a mouse model"*
**作者**: Jorgensen, N.D., Andresen, J.M., Lagalwar, S., et al. (2016)
**摘要**: 研究使用ATXN1抗体检测反义寡核苷酸(ASO)治疗后小鼠模型中突变ATXN1蛋白水平的降低,证实ASO可通过减少毒性蛋白表达改善运动协调性和神经病理表型。
---
**备注**:如需具体实验细节(如抗体克隆号、应用场景),建议查阅原文方法学部分。
The ATXN1 antibody is a crucial tool in neuroscience and molecular biology research, primarily targeting the ataxin-1 protein encoded by the *ATXN1* gene. ATXN1 is best known for its role in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1), an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the *ATXN1* gene. This mutation leads to an elongated polyglutamine tract in the ataxin-1 protein, resulting in its misfolding, aggregation, and neuronal toxicity, particularly in cerebellar Purkinje cells and brainstem nuclei.
ATXN1 antibodies are widely used to detect and study the expression, localization, and post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation, ubiquitination) of wild-type and mutant ataxin-1 in cellular and animal models. These antibodies aid in elucidating disease mechanisms, such as protein aggregation dynamics, interactions with co-factors (e.g., CIC, Capicua), and pathways contributing to neurodegeneration. Commercial ATXN1 antibodies are typically developed in rabbit or mouse hosts, targeting specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal, polyQ region). Their applications span Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation assays.
Research using ATXN1 antibodies has advanced therapeutic strategies, including gene silencing and small-molecule interventions targeting toxic ataxin-1 species. However, cross-reactivity with homologous proteins or polyQ sequences remains a potential limitation, necessitating careful validation. Overall, ATXN1 antibodies remain indispensable for understanding SCA1 pathology and developing targeted therapies.
×